* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1_chemh
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Thermomechanical analysis wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Nanochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
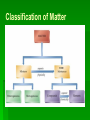
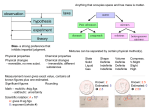
Matter and Change Chapter 1 Chemistry is a Physical Science ●Chemistry: is the study of the composition, structure, and properties of matter, the processes that matter undergoes, and the energy changes that accompany these processes. Matter and Its Properties ●Atom: smallest unit of an element that maintains the chemical identity of that element. ●Mass: measure of the amount of matter. ●Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space. ●Element: a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler, stable substances and is made of one type of atom. ●Compound: substance that can be broken down into simpler stable substances. Made from the atoms of two or more elements that are chemically bonded. ● Mixtures are made from 2 or more substances that retain their identities. o Homogeneous = same throughout oHeterogeneous = not uniform ● Pure Substance has fixed composition and the same characteristic properties throughout. o Compound = 2 or more elements chemically bonded together o Element = identical atoms throughout. Classification of Matter PURE Properties and Changes in Matter ●Extensive properties: depend on the amount of matter that is present. (volume, mass, etc) ●Intensive properties: do not depend on the amount of matter present. (melting point, boiling point, etc) ●Physical Property: characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance. (melting, boiling, etc) oPhysical Change: change that does not involve a change in the identity of the substance. (cutting, melting, etc) Chemical Properties and Chemical Changes ● Chemical properties is the substance’s ability to change into another substance. CO2 H 2O (Oxygen) ● Chemical Change ( ) or Reaction is when substances are converted into other substances o Reactants: the ‘ingredients’ – wood, oxygen & heat o Products: what are formed – ash, CO2 & steam Change of state: physical change from one state to another. ●Solid: definite volume definite shape ●Liquid: definite volume indefinite shape ●Gas: neither definite volume nor shape ●Plasma: high-temperature state where most atoms lose their electrons. Elements ● Groups/families: vertical columns o Similar chemical properties ● Periods: horizontal rows o Physical/chemical properties change regularly across. … … … … ……………………………………………………………………………. … … … … … . … . Types of Elements ●Metals: an element that is a good electrical conductor and heat conductor. Properties: most are solid at room Temperature, malleability, ductile, Tensile strength, luster. ●Nonmetals: poor conductors of heat and electricity. oMany are gases at room temperature. Bromine is a liquid. Carbon, Phosphorous, selenium, sulfur and iodine are solids. oTend to be brittle. ●Metalloids: Has some characteristics of metals and some characteristics of nonmetals. oSolid at room temperature, less malleable, semiconductors, some have luster. Which metalloid is Essential for our Computer-driven Technology? ●Noble Gases: Part of the nonmetals, these elements are gases at room temperature. oGenerally unreactive with other elements