GRAPHITE
... Streak (color when crushed to a powder): Black gray Luster: Metallic to dull Crystal structure: Hexagonal Cleavage: Basal in direction 1,1 Fracture: Conchoidal (smooth shell-like) ...
... Streak (color when crushed to a powder): Black gray Luster: Metallic to dull Crystal structure: Hexagonal Cleavage: Basal in direction 1,1 Fracture: Conchoidal (smooth shell-like) ...
technical report 91 -32
... radioactive elements to the biosphere. Intrusion of water into the repository could lead to leaching of the radioactive elements and migration through the barriers into surface waters from where they could enter the food chain. Government regulations set a limit for radiation doses resulting from su ...
... radioactive elements to the biosphere. Intrusion of water into the repository could lead to leaching of the radioactive elements and migration through the barriers into surface waters from where they could enter the food chain. Government regulations set a limit for radiation doses resulting from su ...
File
... electron with relative ease to form M+ cations when in ionic compounds. They all are easily oxidized. Therefore, in order to prepare the pure metals, alkali metals must be produced in the absence of materials (H2O, O2) that are capable of oxidizing them. The method of preparation is electrochemical ...
... electron with relative ease to form M+ cations when in ionic compounds. They all are easily oxidized. Therefore, in order to prepare the pure metals, alkali metals must be produced in the absence of materials (H2O, O2) that are capable of oxidizing them. The method of preparation is electrochemical ...
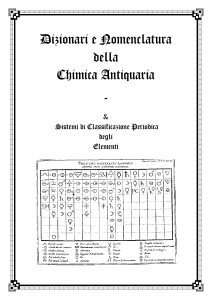
A Dictionary of the New Chymical Nomenclature
... Sulphureous acid Volatile sulphureous acid Phlogisticated vitriolic acid Spirit of sulphur ...
... Sulphureous acid Volatile sulphureous acid Phlogisticated vitriolic acid Spirit of sulphur ...
The d-Block Elements
... half-filled 5s subshell, with 5s14d4 and 5s14d6 valence electron configurations, respectively. Further complications occur among the third-row transition metals, in which the 4f, 5d, and 6s orbitals are extremely close in energy. Although La has a 6s25d1 valence electron configuration, the valence e ...
... half-filled 5s subshell, with 5s14d4 and 5s14d6 valence electron configurations, respectively. Further complications occur among the third-row transition metals, in which the 4f, 5d, and 6s orbitals are extremely close in energy. Although La has a 6s25d1 valence electron configuration, the valence e ...
File - UTeach Dallas Project
... Knowledge with understanding The candidates should be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding in relation to:(a) scientific phenomena, facts, concepts, theories and laws. (b) scientific terminology, use of symbols, quantities and units. (c) scientific apparatus and instruments and their safe ...
... Knowledge with understanding The candidates should be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding in relation to:(a) scientific phenomena, facts, concepts, theories and laws. (b) scientific terminology, use of symbols, quantities and units. (c) scientific apparatus and instruments and their safe ...
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry
... 2 The relative importance of different elements From an academic point of view, all elements might be said to be equally important. The chemistry of each has to be understood in detail if the chemistry of matter as a whole is to be understood in detail. From the point of view of the world at large, ...
... 2 The relative importance of different elements From an academic point of view, all elements might be said to be equally important. The chemistry of each has to be understood in detail if the chemistry of matter as a whole is to be understood in detail. From the point of view of the world at large, ...
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry
... 2 The relative importance of different elements From an academic point of view, all elements might be said to be equally important. The chemistry of each has to be understood in detail if the chemistry of matter as a whole is to be understood in detail. From the point of view of the world at large, ...
... 2 The relative importance of different elements From an academic point of view, all elements might be said to be equally important. The chemistry of each has to be understood in detail if the chemistry of matter as a whole is to be understood in detail. From the point of view of the world at large, ...
Chemistry – 5071
... on the understanding and application of scientific concepts and principles. This approach has been adopted in recognition of the need of students to develop skills that will be of long term value in an increasing technological world rather than focusing on large quantities of actual material which m ...
... on the understanding and application of scientific concepts and principles. This approach has been adopted in recognition of the need of students to develop skills that will be of long term value in an increasing technological world rather than focusing on large quantities of actual material which m ...
p-BLOCK ELEMENTS - einstein classes
... B2O3 is a typical non-metallic oxide and is acidic in its properties. It is the anhydride of orthoboric acid, and it reacts with basic (metallic) oxides, forming salts called borates or metaborates, for example : CoO + B2O3 Co(BO2)2 cobalt metaborate (blue colour). However, it is possible to formc ...
... B2O3 is a typical non-metallic oxide and is acidic in its properties. It is the anhydride of orthoboric acid, and it reacts with basic (metallic) oxides, forming salts called borates or metaborates, for example : CoO + B2O3 Co(BO2)2 cobalt metaborate (blue colour). However, it is possible to formc ...
C5 Chemicals of the Natural Environment SOW
... Students begin by learning about the substances found in the air, which are molecular, and hence find out about covalent bonding and the properties of simple molecular substances. Next we explore the ionic compounds found in seawater, in particular how the ionic bond forms ionic crystals. Students t ...
... Students begin by learning about the substances found in the air, which are molecular, and hence find out about covalent bonding and the properties of simple molecular substances. Next we explore the ionic compounds found in seawater, in particular how the ionic bond forms ionic crystals. Students t ...
BARIUM NITRATE
... elemental sulfur and various anions of sulfur including sulfite, thiosulfate, polysulfides and sulfate. The yellow color of barium sulfide solution is attributed to the presence of dissolved elemental sulfur that results from its slow oxidation in the air. In the presence of an oxidizing agent, bari ...
... elemental sulfur and various anions of sulfur including sulfite, thiosulfate, polysulfides and sulfate. The yellow color of barium sulfide solution is attributed to the presence of dissolved elemental sulfur that results from its slow oxidation in the air. In the presence of an oxidizing agent, bari ...
Redox speciation analysis of antimony in soil extracts by hydride
... antimony determination. Therefore, the selective determination of Sb(III) was carried out in citric acid–HCl medium, using the analyte addition technique. Total antimony in soil extracts was determined using the standard calibration technique after reducing Sb(V) to Sb(III) at room temperature with ...
... antimony determination. Therefore, the selective determination of Sb(III) was carried out in citric acid–HCl medium, using the analyte addition technique. Total antimony in soil extracts was determined using the standard calibration technique after reducing Sb(V) to Sb(III) at room temperature with ...
Multiwalled Boron Nitride Nanotubes: Growth, Properties, and
... by Golberg et al. [44]. Single crystal c-BN specimens were laser heated in a diamond anvil cell under high nitrogen pressures. TEM and other characterization techniques confirmed the product to be BNNTs. Another laser-based technique was oven-laser ablation method [20]. The target material was prepa ...
... by Golberg et al. [44]. Single crystal c-BN specimens were laser heated in a diamond anvil cell under high nitrogen pressures. TEM and other characterization techniques confirmed the product to be BNNTs. Another laser-based technique was oven-laser ablation method [20]. The target material was prepa ...
Chapter - WTPS.org
... • the most abundant elements of the Earth’s crust are O and Si • silicates are covalent atomic solids of Si and O and minor amounts of other elements found in rocks, soils, and clays silicates have variable structures – leading to the variety of properties found in rocks, clays, and soils Tro, Ch ...
... • the most abundant elements of the Earth’s crust are O and Si • silicates are covalent atomic solids of Si and O and minor amounts of other elements found in rocks, soils, and clays silicates have variable structures – leading to the variety of properties found in rocks, clays, and soils Tro, Ch ...
Chapter22_LEC
... • the most abundant elements of the Earth’s crust are O and Si • silicates are covalent atomic solids of Si and O and minor amounts of other elements found in rocks, soils, and clays silicates have variable structures – leading to the variety of properties found in rocks, clays, and soils Tro, Ch ...
... • the most abundant elements of the Earth’s crust are O and Si • silicates are covalent atomic solids of Si and O and minor amounts of other elements found in rocks, soils, and clays silicates have variable structures – leading to the variety of properties found in rocks, clays, and soils Tro, Ch ...
Learning Outcomes
... (b) describe, with the aid of diagrams, the structure of an atom as containing protons and neutrons (nucleons) in the nucleus and electrons arranged in shells (energy levels) (Knowledge of s, p, d and f classification is not required; a copy of the Periodic Table will be available in Papers 1 and 2) ...
... (b) describe, with the aid of diagrams, the structure of an atom as containing protons and neutrons (nucleons) in the nucleus and electrons arranged in shells (energy levels) (Knowledge of s, p, d and f classification is not required; a copy of the Periodic Table will be available in Papers 1 and 2) ...
Magnesium based ternary metal hydrides containing alkali and
... MgH2 . Notable exceptions are the tetrahedral H configurations (CN = 4) in -K2 SO4 -type hydrides (Rb2 MgH4 , lp-Cs2 MgH4 ) and Cs3 CoCl5 -type hydrides (Cs3 MgH5 ), and the pentagonal bipyramidal H configuration (CN = 7) in Ae4 Mg3 H14 (Ae = Ca, Yb). As expected, the MgH6 octahedra tend to be isol ...
... MgH2 . Notable exceptions are the tetrahedral H configurations (CN = 4) in -K2 SO4 -type hydrides (Rb2 MgH4 , lp-Cs2 MgH4 ) and Cs3 CoCl5 -type hydrides (Cs3 MgH5 ), and the pentagonal bipyramidal H configuration (CN = 7) in Ae4 Mg3 H14 (Ae = Ca, Yb). As expected, the MgH6 octahedra tend to be isol ...
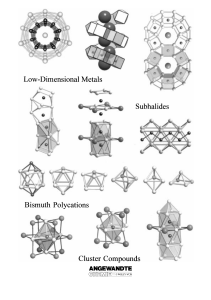
From the Metal to the Molecule
... variation in metal/nonmetal ratios and range from partially oxidized intermetallic phases to complex salts and molecular solids. Consequently, there is a remarkable wealth of structural motifs that are not simply different arrangements of identical building blocks, but generally represent unique str ...
... variation in metal/nonmetal ratios and range from partially oxidized intermetallic phases to complex salts and molecular solids. Consequently, there is a remarkable wealth of structural motifs that are not simply different arrangements of identical building blocks, but generally represent unique str ...
CHEMISTRY OF p-ELEMENTS - Львівський національний
... The elements of p-series of the Periodic table are the representative elements of III – VIII groups. Most of p-elements are of a vital significance for living systems. Five of them (carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus) as well as hydrogen (s-element) are the structural material for bio s ...
... The elements of p-series of the Periodic table are the representative elements of III – VIII groups. Most of p-elements are of a vital significance for living systems. Five of them (carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus) as well as hydrogen (s-element) are the structural material for bio s ...
metalloids 109 - Technical Learning College
... CEU Course Description Metalloids 109 Course Description Arsenic, boron, silicon, germanium, antimony and tellurium are commonly classified as metalloids. One or more from among selenium, polonium or astatine are sometimes added to the list. Boron is sometimes excluded from the list, by itself or t ...
... CEU Course Description Metalloids 109 Course Description Arsenic, boron, silicon, germanium, antimony and tellurium are commonly classified as metalloids. One or more from among selenium, polonium or astatine are sometimes added to the list. Boron is sometimes excluded from the list, by itself or t ...
Chapter 23 Metals and Metallurgy
... Intermetallic Compounds • Intermetallic compounds are homogeneous alloys with definite properties and compositions. • An example is Co5Sm, – which is used for permanent magnets in headsets and Metals speakers. and Metallurgy © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... Intermetallic Compounds • Intermetallic compounds are homogeneous alloys with definite properties and compositions. • An example is Co5Sm, – which is used for permanent magnets in headsets and Metals speakers. and Metallurgy © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Novel Class of Heterometallic Cubane and Boride Clusters
... bound to molybdenum and boron. Cluster 5 represents an unprecedented metal-rich metallaborane cluster with a cubane core. The dimolybdaheteroborane 2 was found to be very reactive toward metal carbonyl compounds, and as a result, mild pyrolysis of 2 with [Fe2(CO)9] yielded distorted cubane cluster [ ...
... bound to molybdenum and boron. Cluster 5 represents an unprecedented metal-rich metallaborane cluster with a cubane core. The dimolybdaheteroborane 2 was found to be very reactive toward metal carbonyl compounds, and as a result, mild pyrolysis of 2 with [Fe2(CO)9] yielded distorted cubane cluster [ ...
Chemistry
... 440 BC, the Greek philosopher Leucippus and his pupil Democritus coined the term atomos to describe the smallest particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, the chemist John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made ...
... 440 BC, the Greek philosopher Leucippus and his pupil Democritus coined the term atomos to describe the smallest particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, the chemist John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made ...
Chapter 22 - 2012 Book Archive
... Group 13 is the first group to span the dividing line between metals and nonmetals, so its chemistry is more diverse than that of groups 1 and 2, which include only metallic elements. Except for the lightest element (boron), the group 13 elements are all relatively electropositive; that is, they ten ...
... Group 13 is the first group to span the dividing line between metals and nonmetals, so its chemistry is more diverse than that of groups 1 and 2, which include only metallic elements. Except for the lightest element (boron), the group 13 elements are all relatively electropositive; that is, they ten ...