GROUP 13 ELEMENTS -THE BORON FAMILY -
... network structure. – The other elements are considerably larger than boron and consequently are more ionic and metallic in character. ...
... network structure. – The other elements are considerably larger than boron and consequently are more ionic and metallic in character. ...
Reactions of common metals and properties of
... resembles that of the proton, H+, but there are more differences than similarities. Hydrogen also forms an anion, the hydride ion, H-, and many metals, including the alkali and alkaline earth metals form salt-like hydrides, such as NaH. Such hydrides have similar crystal structures to alkali halides ...
... resembles that of the proton, H+, but there are more differences than similarities. Hydrogen also forms an anion, the hydride ion, H-, and many metals, including the alkali and alkaline earth metals form salt-like hydrides, such as NaH. Such hydrides have similar crystal structures to alkali halides ...
I. Properties of Matter
... group 8A elements 14. Metalloids – elements with physical and chemical properties of both metals and nonmetals; these border the “stair step” between the metals and ...
... group 8A elements 14. Metalloids – elements with physical and chemical properties of both metals and nonmetals; these border the “stair step” between the metals and ...
Lecture 7
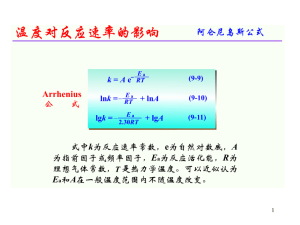
... Going down the group the cations formed get bigger. This means that the positive charge is spread over a larger volume and so is less concentrated. A small ion with its concentrated charge has a high charge density. This high charge density gives the ion the ability to distort or polarize nearby ani ...
... Going down the group the cations formed get bigger. This means that the positive charge is spread over a larger volume and so is less concentrated. A small ion with its concentrated charge has a high charge density. This high charge density gives the ion the ability to distort or polarize nearby ani ...
Chapter 1 Chemistry: The Study of Matter
... Compounds can be broken down by chemical methods When they are broken down, the components have completely different properties than the compound. ...
... Compounds can be broken down by chemical methods When they are broken down, the components have completely different properties than the compound. ...
Presentation
... In the next few slides we will be looking at how to write formulas and names for three different types of chemical compounds: • 1. IONIC COMPOUNDS • 2. MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS • 3. ACIDS *Each type will have a set of rules that we must follow to correctly represent the substance. ...
... In the next few slides we will be looking at how to write formulas and names for three different types of chemical compounds: • 1. IONIC COMPOUNDS • 2. MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS • 3. ACIDS *Each type will have a set of rules that we must follow to correctly represent the substance. ...
CHEMISTRY The Central Science 9th Edition
... and electricity , some are gasses and some are brittle solids. ...
... and electricity , some are gasses and some are brittle solids. ...
13.IVA group. Carbon and Silicon and their compounds.
... Silicon is a solid at room temperature, with relatively high melting and boiling points of approximately 1,400 and 2,800 degrees Celsius respectively. With a relatively high thermal conductivity of 149 W·m−1·K−1, silicon conducts heat well and as a result is not often used to insulate hot objects. I ...
... Silicon is a solid at room temperature, with relatively high melting and boiling points of approximately 1,400 and 2,800 degrees Celsius respectively. With a relatively high thermal conductivity of 149 W·m−1·K−1, silicon conducts heat well and as a result is not often used to insulate hot objects. I ...
p-Block Elements, Part 1
... Very pure silicon (<1 ppb impurity) is required for electronics applications. ...
... Very pure silicon (<1 ppb impurity) is required for electronics applications. ...
Chapter One Powerpoint - Geneva Area City Schools
... Introduction to the Periodic Table • All known elements are organized into a chart known as the periodic table • The vertical columns of the periodic table are called groups, or families. • Each group contains elements with similar chemical properties. • The horizontal rows of elements in the perio ...
... Introduction to the Periodic Table • All known elements are organized into a chart known as the periodic table • The vertical columns of the periodic table are called groups, or families. • Each group contains elements with similar chemical properties. • The horizontal rows of elements in the perio ...
ionic bond. - cloudfront.net
... malleable (can be hammered into sheets) and are ductile (drawn into wires). ...
... malleable (can be hammered into sheets) and are ductile (drawn into wires). ...
Communicating Research to the General Public
... When asked to describe inorganic chemistry, one of the easiest responses is to describe it as the opposite of organic chemistry, as the name implies, and then describe organic chemistry. However, this does an injustice to the field of inorganic chemistry, which we interact with on a daily basis and ...
... When asked to describe inorganic chemistry, one of the easiest responses is to describe it as the opposite of organic chemistry, as the name implies, and then describe organic chemistry. However, this does an injustice to the field of inorganic chemistry, which we interact with on a daily basis and ...
pblock - Chemistry Courses
... Very pure silicon (<1 ppb impurity) is required for electronics applications. ...
... Very pure silicon (<1 ppb impurity) is required for electronics applications. ...
Day 13 Main Group Pt 1
... 5. Group IV. Carbon, silicon, germanium, tin and lead Electronegativities of the Elements. The main group elements and their electronegativities are shown in the table below. Much of the main group chemistry is determined by whether the compounds are ionic or covalent. The alkali metals and alkaline ...
... 5. Group IV. Carbon, silicon, germanium, tin and lead Electronegativities of the Elements. The main group elements and their electronegativities are shown in the table below. Much of the main group chemistry is determined by whether the compounds are ionic or covalent. The alkali metals and alkaline ...
Lecture 2-Extraction of Elements
... Priming the reaction with Mg-ribbon and barium peroxide / a KNO3+S+Al pellet is necessary. The reduction is usually exothermic. Once initiated, the whole mass gets reduced spontaneously. Alloy formation with Al can take place in some cases. ...
... Priming the reaction with Mg-ribbon and barium peroxide / a KNO3+S+Al pellet is necessary. The reduction is usually exothermic. Once initiated, the whole mass gets reduced spontaneously. Alloy formation with Al can take place in some cases. ...
Chapter 1 Chemistry: The Study of Matter
... When charcoal (carbon) burns, it combines with oxygen in the air to form carbon dioxide. The charcoal and oxygen no longer exists in their original form. ...
... When charcoal (carbon) burns, it combines with oxygen in the air to form carbon dioxide. The charcoal and oxygen no longer exists in their original form. ...
ch22 lecture 7e
... elements are continuously cycled in various forms between different regions of the Earth’s crust. Elements are cycled through physical, biological, and chemical pathways. The most important of these cycles from the perspective of living organisms are the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles. ...
... elements are continuously cycled in various forms between different regions of the Earth’s crust. Elements are cycled through physical, biological, and chemical pathways. The most important of these cycles from the perspective of living organisms are the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles. ...
ch22_lecture_6e_final
... elements are continuously cycled in various forms between different regions of the Earth’s crust. Elements are cycled through physical, biological, and chemical pathways. The most important of these cycles from the perspective of living organisms are the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles. ...
... elements are continuously cycled in various forms between different regions of the Earth’s crust. Elements are cycled through physical, biological, and chemical pathways. The most important of these cycles from the perspective of living organisms are the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles. ...
g - Santa Rosa Junior College
... elements are continuously cycled in various forms between different regions of the Earth’s crust. Elements are cycled through physical, biological, and chemical pathways. The most important of these cycles from the perspective of living organisms are the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles. ...
... elements are continuously cycled in various forms between different regions of the Earth’s crust. Elements are cycled through physical, biological, and chemical pathways. The most important of these cycles from the perspective of living organisms are the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles. ...
The s-Block Elements - GCG-42
... BeCl2 is essentially covalent, with comparatively low m.pt. The lower members in group II form essentially ionic chlorides, with Mg having intermediate properties. ...
... BeCl2 is essentially covalent, with comparatively low m.pt. The lower members in group II form essentially ionic chlorides, with Mg having intermediate properties. ...
CHAPTER 2
... -Carbon (C) is the “element of life” CO2 carbonate-limestone, coral, shells fossil fuels-coal, petroleum, natural gas -Silicon (Si) is found as gemstones, glass, and sand -Lead (Pb) was used as water pipes, paint, and in gasoline -form compounds of analogous chemical formulas ...
... -Carbon (C) is the “element of life” CO2 carbonate-limestone, coral, shells fossil fuels-coal, petroleum, natural gas -Silicon (Si) is found as gemstones, glass, and sand -Lead (Pb) was used as water pipes, paint, and in gasoline -form compounds of analogous chemical formulas ...
Sub Unit Plan 1 Chem Periodic Table
... have the same atomic number. Elements cannot be broken down by chemical change. 3.1v Elements can be classified by their properties and located on the Periodic Table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te), and noble gases. 3.1w Elements can be differentiated by physical properties. ...
... have the same atomic number. Elements cannot be broken down by chemical change. 3.1v Elements can be classified by their properties and located on the Periodic Table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te), and noble gases. 3.1w Elements can be differentiated by physical properties. ...
the Main-Group Metals - McQuarrie General Chemistry
... is a relatively rare element but occurs as localized surface deposits in the mineral beryl (Figure I.2). Essentially unlimited quantities of magnesium are readily available in seawater, where Mg2+(aq) occurs at an appreciable concentration. Calcium, strontium, and barium rank 5th, 18th, and 19th in ...
... is a relatively rare element but occurs as localized surface deposits in the mineral beryl (Figure I.2). Essentially unlimited quantities of magnesium are readily available in seawater, where Mg2+(aq) occurs at an appreciable concentration. Calcium, strontium, and barium rank 5th, 18th, and 19th in ...
Dmitri Mendeleev
... Metalloids are elements that possess some properties of metals and some of non-metals. The most important metalloids are silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge) which are used extensively in computer chips. ...
... Metalloids are elements that possess some properties of metals and some of non-metals. The most important metalloids are silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge) which are used extensively in computer chips. ...