Chemical Bonds Study Guide Answer Key
... Alloys- combination of 2 or more elements, at least one is a metal Examples- steel, sterling silver, 14K gold ...
... Alloys- combination of 2 or more elements, at least one is a metal Examples- steel, sterling silver, 14K gold ...
PPTB&W - Gmu - George Mason University
... ● Recall: A1 oxides (ionic charge +1 and more metallic) are more basic than A2 oxides (ionic charge +2 and less metallic) ● In general, oxides with the element in a lower oxidation state (less positive) are more basic than oxides with the element in a higher oxidation state ● For Indium oxides in Gr ...
... ● Recall: A1 oxides (ionic charge +1 and more metallic) are more basic than A2 oxides (ionic charge +2 and less metallic) ● In general, oxides with the element in a lower oxidation state (less positive) are more basic than oxides with the element in a higher oxidation state ● For Indium oxides in Gr ...
ch14 lecture 7e
... Highlights of Boron Chemistry All boron compounds are covalent, and B forms a variety of network covalent compounds with other elements. Boron is often electron-deficient in compounds, and acts effectively as a Lewis acid since it can accept an e- pair. BF3(g) + :NH3(g) → F3B–NH3(g) Boron forms bri ...
... Highlights of Boron Chemistry All boron compounds are covalent, and B forms a variety of network covalent compounds with other elements. Boron is often electron-deficient in compounds, and acts effectively as a Lewis acid since it can accept an e- pair. BF3(g) + :NH3(g) → F3B–NH3(g) Boron forms bri ...
PPT - George Mason University
... Recall: A1 oxides (ionic charge +1 and more metallic) are more basic than A2 oxides (ionic charge +2 and less metallic) In general, oxides with the element in a lower oxidation state (less positive) are more basic than oxides with the element in a higher oxidation state For Indium oxides in Gr ...
... Recall: A1 oxides (ionic charge +1 and more metallic) are more basic than A2 oxides (ionic charge +2 and less metallic) In general, oxides with the element in a lower oxidation state (less positive) are more basic than oxides with the element in a higher oxidation state For Indium oxides in Gr ...
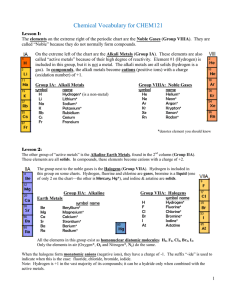
Vocabulary CHEM121
... up a chemical unit (compound, ion, etc.). The formula includes symbols of each element and numerical subscripts to show the number of each atom present. If only one atom is present, no subscript is used. Formulas of binary salts: (two-element compounds formed from a metal and a non-metal) Remember t ...
... up a chemical unit (compound, ion, etc.). The formula includes symbols of each element and numerical subscripts to show the number of each atom present. If only one atom is present, no subscript is used. Formulas of binary salts: (two-element compounds formed from a metal and a non-metal) Remember t ...
Unit 3 Review Packet
... substances and observed bubbles. What can you conclude about why the bubbles formed? a. A chemical reaction produced a gas. b. Only a physical change occurred. c. The temperature of the substance changed. d. No chemical reaction took place. Which of the following observed properties is most reliable ...
... substances and observed bubbles. What can you conclude about why the bubbles formed? a. A chemical reaction produced a gas. b. Only a physical change occurred. c. The temperature of the substance changed. d. No chemical reaction took place. Which of the following observed properties is most reliable ...
Use the following to answer questions 1-14:
... electrons in the valence shell. ____ 2. Metallic elements form cations. ____ 3. Cations are negatively charged ions. ____ 4. Valence electrons are located in the outermost electron shell of the atom. ____ 5. Noble gases are very stable; other elements give up, gain, or share electrons to acquire a v ...
... electrons in the valence shell. ____ 2. Metallic elements form cations. ____ 3. Cations are negatively charged ions. ____ 4. Valence electrons are located in the outermost electron shell of the atom. ____ 5. Noble gases are very stable; other elements give up, gain, or share electrons to acquire a v ...
NON METALS- SILICON
... 2. Magnesium oxide and silicon are formed. 3. The product is washed with dilute hydrochloric acid to ...
... 2. Magnesium oxide and silicon are formed. 3. The product is washed with dilute hydrochloric acid to ...
Study Island Copyright © 2012 Study Island
... 15. Which of the following is true about a compound and its elements? A. The properties of a compound are the same as the properties of its elements. B. The elements all share identical properties, but their properties are different than the compound's properties. C. The properties of a compound are ...
... 15. Which of the following is true about a compound and its elements? A. The properties of a compound are the same as the properties of its elements. B. The elements all share identical properties, but their properties are different than the compound's properties. C. The properties of a compound are ...
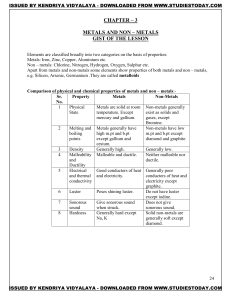
METALS AND NON – METALS Concepts
... GIST OF THE LESSON Elements are classified broadly into two categories on the basis of properties: Metals: Iron, Zinc, Copper, Aluminium etc. Non – metals: Chlorine, Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sulphur etc. Apart from metals and non-metals some elements show properties of both metals and non – metal ...
... GIST OF THE LESSON Elements are classified broadly into two categories on the basis of properties: Metals: Iron, Zinc, Copper, Aluminium etc. Non – metals: Chlorine, Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sulphur etc. Apart from metals and non-metals some elements show properties of both metals and non – metal ...
Scientific Method - Virtual Medical Academy
... * Shiny, ductile. * Good conductors of heat and electricity. Nonmetals *Located to the right of the heavy line. * Dull and brittle. * Poor conductors. ...
... * Shiny, ductile. * Good conductors of heat and electricity. Nonmetals *Located to the right of the heavy line. * Dull and brittle. * Poor conductors. ...
Scientific Method - Virtual Medical Academy
... * Shiny, ductile. * Good conductors of heat and electricity. Nonmetals *Located to the right of the heavy line. * Dull and brittle. * Poor conductors. ...
... * Shiny, ductile. * Good conductors of heat and electricity. Nonmetals *Located to the right of the heavy line. * Dull and brittle. * Poor conductors. ...
Chapter 1 - Manual Science Chemistry/Physics
... o Each element has characteristic properties o The vertical columns of the periodic table are called groups, or families. Each group’s elements have similar properties. o The horizontal rows of elements in the periodic table are called periods. Physical and chemical properties change somewhat re ...
... o Each element has characteristic properties o The vertical columns of the periodic table are called groups, or families. Each group’s elements have similar properties. o The horizontal rows of elements in the periodic table are called periods. Physical and chemical properties change somewhat re ...
Chapters 19 & 20
... possible valence electrons from one in group 1A to eight in group 8A. The valence electrons of representative elements are in s or p orbitals. Metals tend to lose their valence electrons to form cations with a configuration of the noble gas from the preceding period Nonmetals tend to gain electrons ...
... possible valence electrons from one in group 1A to eight in group 8A. The valence electrons of representative elements are in s or p orbitals. Metals tend to lose their valence electrons to form cations with a configuration of the noble gas from the preceding period Nonmetals tend to gain electrons ...
Silicon vs. Carbon - Coristines
... Carbon can create four covalent bonds allowing it to link to itself in order to create carbon chains of different lengths/ configurations, or to connect to non-carbon atoms in order to form compounds with unique and specialized chemical properties. ...
... Carbon can create four covalent bonds allowing it to link to itself in order to create carbon chains of different lengths/ configurations, or to connect to non-carbon atoms in order to form compounds with unique and specialized chemical properties. ...
elements in a family have the same number of
... after the element that makes up 78% of our atmosphere. This family includes nonmetals, metalloids, and metals. Atoms in the nitrogen family have 5 valence electrons. They tend to share electrons when they bond. Other elements in this family are phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. ...
... after the element that makes up 78% of our atmosphere. This family includes nonmetals, metalloids, and metals. Atoms in the nitrogen family have 5 valence electrons. They tend to share electrons when they bond. Other elements in this family are phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. ...
MYP 10 PeriodicityWS
... for the alkali metals (Li Cs) and the halogens (FI). 3.2.3. Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies and electronegativities for elements across period 3. 3.3 Chemical properties 3.3.1 Discuss the similarities and differences in the chemical properti ...
... for the alkali metals (Li Cs) and the halogens (FI). 3.2.3. Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies and electronegativities for elements across period 3. 3.3 Chemical properties 3.3.1 Discuss the similarities and differences in the chemical properti ...
Document
... The combination of 2 or more substances to form a compound Only one product General form: element or compound + element or compound compound ...
... The combination of 2 or more substances to form a compound Only one product General form: element or compound + element or compound compound ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood (Pages 735
... *f. COMPOUNDS can be broken down, but because the elements were CHEMICALLY joined together, a CHEMICAL process is necessary to SEPARATE them. *1. Heating breaks down some COMPOUNDS: iron separated from oxygen (e.g.) 2 Fe2O3 + 3 C (are heated) 4 Fe + 3 CO2 (the IRON [Fe] is SEPARATED) *2. Electroly ...
... *f. COMPOUNDS can be broken down, but because the elements were CHEMICALLY joined together, a CHEMICAL process is necessary to SEPARATE them. *1. Heating breaks down some COMPOUNDS: iron separated from oxygen (e.g.) 2 Fe2O3 + 3 C (are heated) 4 Fe + 3 CO2 (the IRON [Fe] is SEPARATED) *2. Electroly ...
CERAMICS MATERIALS - Wits Structural Chemistry
... and NiO have low conductivity that increase with temperature or have such large band gaps that become insulators. The electron-hole migration in these oxides is attributed to the hopping mechanism. The electron or hole hops from one localized metal atom site to the other, and causes the surrounding ...
... and NiO have low conductivity that increase with temperature or have such large band gaps that become insulators. The electron-hole migration in these oxides is attributed to the hopping mechanism. The electron or hole hops from one localized metal atom site to the other, and causes the surrounding ...
Variation in Properties of Group II Compounds
... Each group of elements embodied in the periodic table has their own unique properties. As for group II elements, they are classified as one of the s-block elements, also named as alkaline earth metals. In this essay, the variation in properties of group II elements and their compounds are illustrate ...
... Each group of elements embodied in the periodic table has their own unique properties. As for group II elements, they are classified as one of the s-block elements, also named as alkaline earth metals. In this essay, the variation in properties of group II elements and their compounds are illustrate ...
Chapter 1 Matter on the Atomic Scale
... Nonmetals Occur in all physical states. solids: sulfur, phosphorus, carbon. liquid: bromine. gases: oxygen, helium, nitrogen. ...
... Nonmetals Occur in all physical states. solids: sulfur, phosphorus, carbon. liquid: bromine. gases: oxygen, helium, nitrogen. ...
The ocean is a mixture.
... another and to other metals, but their properties do not fit in with those of any other family. Many transition metals combine chemically with oxygen to form compounds called oxides. They have one or two electrons in the outer level Reactivity: less reactive than alkaline-earth metals Properties: Sh ...
... another and to other metals, but their properties do not fit in with those of any other family. Many transition metals combine chemically with oxygen to form compounds called oxides. They have one or two electrons in the outer level Reactivity: less reactive than alkaline-earth metals Properties: Sh ...
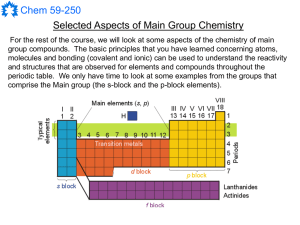
Main Group Notes 1
... Much of the important chemistry of the group 16 elements can be understood on the basis of their electronic structure and electronegativity. Since the elements have a [core]ns2 np4 electron configuration, neutral group 16 compounds can form up to six bonds. This provides for common oxidation state f ...
... Much of the important chemistry of the group 16 elements can be understood on the basis of their electronic structure and electronegativity. Since the elements have a [core]ns2 np4 electron configuration, neutral group 16 compounds can form up to six bonds. This provides for common oxidation state f ...