* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ionic bond. - cloudfront.net
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Oxidation state wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Shape-memory alloy wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Cation–pi interaction wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Crystal structure wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Bent's rule wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Halogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Ionic compound wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Ionic liquid wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
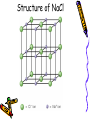
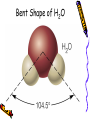
Chapter 6B: Chemical Bonding General Chemistry Mr. Mata Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net Standard 2a • Atoms exchange electrons to form an ionic bond. Essential Question • How do electrons behave during ionic bonding? 6-3 Ionic Bonding and Compounds • Ionic Compound- composed of + and ions combined so charges are equal. (Metal + nonmetal) • Formula Unit- simplest group of atoms form an ionic compound. Cation Formation • Main group metals lose all their valence e-’s to form cations (+): • This loss of electrons is called oxidation. . • Na Na1+ + 1esodium • Mg: Mg2+ + 2 emagnesium . • : Al Al 3+ + 3 ealuminum Anion Formation • Non-metals gain e-’s to form anions (-). • This process is called reduction. Cl O N 123- chloride (gain 1 e-) oxide (gain 2 e-’s) nitride (gain 3 e-’s) Ionic Bond • • • • - charges are attracted to + charges. - anions are attracted to + cations. The result is an ionic bond. 3-D crystal lattice of anions & cations formed. Structure of NaCl Properties of Ionic Compounds • • • • • Crystals form. High melting point & boiling point. Brittle (breaks easily). Melt when heated (very high temps!) Aqueous solutions conduct electricity. (solutions mixed in water) Electronegativity (EN) • Atoms to the right & top of Periodic Table have greater EN values. • F most EN of elements (EN = 4.0). • Fr least EN of elements (EN = O.7). • Cl =3.0 H = 2.1 S = 2.5 • O = 3.5 Na = 0.9 Br = 2.8 • C = 2.5 N = 3.0 I = 2.5 Polar & Nonpolar Bonds – H-H is non-polar because H & H have the same EN’s. (EN diff. = 0) – Cl-Cl is non-polar because Cl & Cl have the same EN’s. (EN diff. = 0) – H-Cl is polar because H & Cl have different EN’s. ( H = 2.1, Cl = 3.0 ) Predicting Bond Type • There is a continuum between non-polar covalent bonds to ionic bonds. • Non-polar bond; little difference in EN between atoms. (EN diff. = 0 – 0.3) • Ionic bonds; greatest EN diff between atoms. (ΔEN > 1.7) • Polar covalent bonds; in between EN diff between atoms. (EN diff. = 0.3 – 1.7) Ionic vs. Covalent Bonds Ionic Bonds • • • • • • • Exchange e-’s Metal + non-metal 3-D units (crystals) high mp/bp Brittle, melt Ex: NaCl conduct electricity Covalent Bonds •Sharing e-’s •non-metal + non-metal •Molecular (low mp/bp) • ex: CO2, Cl2 •Macromolecular (high mp/bp) •Ex: C(diamond), SiO2 •Non conductors Ionic Bonding in NaCl Ionic Bonding in NaCl 6-4 Metallic Bonding • Metals- conduct heat, have low ionization energy • Low EN; give up electrons easily. • Metals have luster (shine), are malleable (can be hammered into sheets) and are ductile (drawn into wires). Metallic Bonding • Metallic Bonding - type of bonding found in metallic crystals. • 3-D lattice of positive ions. • remain fixed in a crystal lattice. • loosely-held valence e-’s move freely throughout the crystal. • The fluid-like movements of valence e-’s make metals good conductors of heat and electricity. Metallic Bonding Metal Alloys • Alloys -metallic substances composed of two or more elements; at least one of these elements is a metal. • Alloys are important because the properties of an alloy are often superior to those of its component elements. Common Metal Alloys – Stainless steel (composed of Fe, Cr, C, Ni) – Sterling silver (composed of Ag & Cu) – 14 karat gold (composed of Au & Cu) Note: Pure gold too soft for jewelry!) – Brass/bronze (composed of Cu & Zn) 6-5 Molecular Geometry • E- pairs around the central atom stay as far apart as possible. • Consider non-bonding (lone pairs) as well as bonding e-’s. • E- pairs in single, double and triple bonds are treated as single e- clouds. VSEPR Theory • Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) • Two e- clouds around a central atom form a linear shape as in CO2 and BeF2 • Three e- clouds form a trigonal planar shape as in BF3 VSEPR Theory • The shape formed by the four e- pairs is called a tetrahedron as in CH4. • In water, H2O, two of the corners are occupied by hydrogens. • Gives water molecule its bent shape. Structure of H2O • Bonded e- pairs are often represented as lines: • : • So H2O would look like this: :O H • H • There are a total of 2 e- pairs which try to get as far away from each other as possible. Result = bent shape. Bent Shape of H2O Hydrogen Bonding • Hydrogen bonding - strongest of the intermolecular bonds (bonds between molecules). • Hydrogen bonding - hydrogen atoms bonded to highly EN elements such as F, O, and N. • Hydrogen bonding - responsible for the relatively high MP & BP of water. Chapter 6B SUTW Prompt • Describe the different properties of ionic bonds and metallic bonds by describing how the electrons interact with each bonding type. • Complete an 8-10 sentence paragraph using the SUTW paragraph format. Hilight using green, yellow, and pink. • Due Date: Tomorrow (start of class).