Clusters: Structure, Energetics, and Dynamics of Intermediate States
... protonated species, parent ions of the original molecular nature, and a variety of metal ions could be produced and investigated. Mixed clusters were soon studied, and extensive data are now available on the solvation of mixed molecular and protonated complexes, in addition to the aforementioned spe ...
... protonated species, parent ions of the original molecular nature, and a variety of metal ions could be produced and investigated. Mixed clusters were soon studied, and extensive data are now available on the solvation of mixed molecular and protonated complexes, in addition to the aforementioned spe ...
Chemical Redox Agents for Organometallic
... redox reactions generally yield larger quantities of products in briefer reaction times, and at higher concentrations, when compared with electrolytic preparations. Except for thin-layer electrochemical cells,7a,b which are very limited in the quantities of reagent that can be produced, preparative ...
... redox reactions generally yield larger quantities of products in briefer reaction times, and at higher concentrations, when compared with electrolytic preparations. Except for thin-layer electrochemical cells,7a,b which are very limited in the quantities of reagent that can be produced, preparative ...
Chemical Redox Agents for Organometallic
... redox reactions generally yield larger quantities of products in briefer reaction times, and at higher concentrations, when compared with electrolytic preparations. Except for thin-layer electrochemical cells,7a,b which are very limited in the quantities of reagent that can be produced, preparative ...
... redox reactions generally yield larger quantities of products in briefer reaction times, and at higher concentrations, when compared with electrolytic preparations. Except for thin-layer electrochemical cells,7a,b which are very limited in the quantities of reagent that can be produced, preparative ...
Spectroscopic Comparisons of the pH Dependencies of Fe
... Fe- and Mn-SODs are dimers or tetramers of identical monomers, which each have one active site containing a single Fe or Mn ion. The overall folds are the same, and in both cases the metal ion is coordinated in a trigonal bipyramid by two His and an Asp- in the equatorial plane and a His and a solve ...
... Fe- and Mn-SODs are dimers or tetramers of identical monomers, which each have one active site containing a single Fe or Mn ion. The overall folds are the same, and in both cases the metal ion is coordinated in a trigonal bipyramid by two His and an Asp- in the equatorial plane and a His and a solve ...
Transition Metal-Modified Zirconium Phosphate Electrocatalysts for
... a number of general strategies, including increasing the number of active sites, increasing the intrinsic through a number of general strategies, including increasing the number of active sites, increasing the activity of each active site, and/or supporting the active material onto suppo ...
... a number of general strategies, including increasing the number of active sites, increasing the intrinsic through a number of general strategies, including increasing the number of active sites, increasing the activity of each active site, and/or supporting the active material onto suppo ...
Visible Light Photoredox Catalysis with Transition
... commercial household light bulb, a significant advantage over the specialized equipment required for processes employing high-energy ultraviolet (UV) light. Additionally, because organic molecules generally do not absorb visible light, there is little potential for deleterious side reactions that mig ...
... commercial household light bulb, a significant advantage over the specialized equipment required for processes employing high-energy ultraviolet (UV) light. Additionally, because organic molecules generally do not absorb visible light, there is little potential for deleterious side reactions that mig ...
Materials perspective on Casimir and van der Waals interactions
... materials themselves. We consider vdW and Casimir phenomena under equilibrium conditions, leaving aside other important effects including nonequilibrium or critical Casimir forces, which arguably warrant a separate review. We begin the discussion with the vdW regime (Sec. II). The most significant a ...
... materials themselves. We consider vdW and Casimir phenomena under equilibrium conditions, leaving aside other important effects including nonequilibrium or critical Casimir forces, which arguably warrant a separate review. We begin the discussion with the vdW regime (Sec. II). The most significant a ...
Amines - ncert
... Lower aliphatic amines are soluble in water because they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. However, solubility decreases with increase in molar mass of amines due to increase in size of the hydrophobic alkyl part. Higher amines are essentially insoluble in water. Considering the electron ...
... Lower aliphatic amines are soluble in water because they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. However, solubility decreases with increase in molar mass of amines due to increase in size of the hydrophobic alkyl part. Higher amines are essentially insoluble in water. Considering the electron ...
Adsorption and desorption
... res: equ. distance when the adatom interacts with one atom only; zM: distance of adatom from surface. ...
... res: equ. distance when the adatom interacts with one atom only; zM: distance of adatom from surface. ...
Noncovalent interactions of molecules with single walled carbon
... Often, rather than using a discrete potential, a continuum approach has been used,19,32,34–36 where the electronic density is assumed to be uniform over the surface of the nanotube. The continuum and discrete approaches give similar values for energy of interaction, usually within a few percent for ...
... Often, rather than using a discrete potential, a continuum approach has been used,19,32,34–36 where the electronic density is assumed to be uniform over the surface of the nanotube. The continuum and discrete approaches give similar values for energy of interaction, usually within a few percent for ...
PDF File
... of both substrate and potential ribozyme ligands can determine whether such groups are indeed ligands for particular metal ions (5, 17, 27). Possible complications that may arise in these analyses, but that do not apply to the Tetrahymena ribozyme, are described in the Supporting Information. Consid ...
... of both substrate and potential ribozyme ligands can determine whether such groups are indeed ligands for particular metal ions (5, 17, 27). Possible complications that may arise in these analyses, but that do not apply to the Tetrahymena ribozyme, are described in the Supporting Information. Consid ...
21 More About Amines • Heterocyclic Compounds
... amine cannot dissociate to form a carbocation or be replaced by a halide ion. Protonated amino groups also cannot be displaced by strongly basic nucleophiles such as HO - because the base would react immediately with the acidic hydrogen, and protonation would convert it into a poor nucleophile. ...
... amine cannot dissociate to form a carbocation or be replaced by a halide ion. Protonated amino groups also cannot be displaced by strongly basic nucleophiles such as HO - because the base would react immediately with the acidic hydrogen, and protonation would convert it into a poor nucleophile. ...
A Model For the Calculation of Solvent ... Reaction Rates for Process Design Purposes
... screen large numbers of molecules in a reasonable time, as well as applicable to a wide range of solvents and reactions and able to provide results that are accurate for process design needs. Solvent effects on reaction rates can be very marked. Reaction rates can vary by several orders of magnitude ...
... screen large numbers of molecules in a reasonable time, as well as applicable to a wide range of solvents and reactions and able to provide results that are accurate for process design needs. Solvent effects on reaction rates can be very marked. Reaction rates can vary by several orders of magnitude ...
Computational investigations of the electronic structure of molecular
... challenging computationally. The main result of the study confirms that the bonding is ionic and that there are few differences in the behaviour of the transition metals. In the fourth chapter the electronic spectrum of NpO22+, NpO2Cl42- and NpO2(OH)42- is calculated using time dependent DFT. TDDFT ...
... challenging computationally. The main result of the study confirms that the bonding is ionic and that there are few differences in the behaviour of the transition metals. In the fourth chapter the electronic spectrum of NpO22+, NpO2Cl42- and NpO2(OH)42- is calculated using time dependent DFT. TDDFT ...
Side Chain Chemistry Mediates Backbone Fragmentation in
... A crown ether based, photolabile radical precursor which forms noncovalent complexes with peptides has been prepared. The peptide/precursor complexes can be electrosprayed, isolated in an ion trap, and then subjected to laser photolysis and collision induced dissociation to generate hydrogen deficie ...
... A crown ether based, photolabile radical precursor which forms noncovalent complexes with peptides has been prepared. The peptide/precursor complexes can be electrosprayed, isolated in an ion trap, and then subjected to laser photolysis and collision induced dissociation to generate hydrogen deficie ...
kinetics, catalysis, and reaction engineering
... catalyst. One possible choice for this catalyst, Pt/Al2O3, is very efficient for hydrocarbon oxidation3-7 and has also been studied extensively for CO oxidation.9-11 The mechanisms for these oxidation reactions involve adsorption of oxygen on the surface of platinum metal. Adsorbed O atoms on platin ...
... catalyst. One possible choice for this catalyst, Pt/Al2O3, is very efficient for hydrocarbon oxidation3-7 and has also been studied extensively for CO oxidation.9-11 The mechanisms for these oxidation reactions involve adsorption of oxygen on the surface of platinum metal. Adsorbed O atoms on platin ...
CHM203 - National Open University of Nigeria
... Note that the hydrogen bonds are indicated by the dash lines whereas the covalent bonds are represented by solid lines. The hydrogen bonding is a stronger interaction as compared to the dipole-dipole interactions but it is weaker than a covalent bond. The strength of a hydrogen bond ranges from 10 t ...
... Note that the hydrogen bonds are indicated by the dash lines whereas the covalent bonds are represented by solid lines. The hydrogen bonding is a stronger interaction as compared to the dipole-dipole interactions but it is weaker than a covalent bond. The strength of a hydrogen bond ranges from 10 t ...
Peter Ertl - American Chemical Society
... The concept of organic substituents and their influence on molecular properties is one of the pillars of modern organic chemistry as well as a basis of QSAR analysis. Prominent examples from this area are the pioneering contribution of Hammett with regard to the effect of substituents on reactivity ...
... The concept of organic substituents and their influence on molecular properties is one of the pillars of modern organic chemistry as well as a basis of QSAR analysis. Prominent examples from this area are the pioneering contribution of Hammett with regard to the effect of substituents on reactivity ...
Chapter 8 "Ionic versus Covalent Bonding"
... where each ion’s charge is represented by the symbol Q. The proportionality constant k is equal to 2.31 × 10−28 J·m.This value of k includes the charge of a single electron (1.6022 × 10−19 C) for each ion. The equation can also be written using the charge of each ion, expressed in coulombs (C), inco ...
... where each ion’s charge is represented by the symbol Q. The proportionality constant k is equal to 2.31 × 10−28 J·m.This value of k includes the charge of a single electron (1.6022 × 10−19 C) for each ion. The equation can also be written using the charge of each ion, expressed in coulombs (C), inco ...
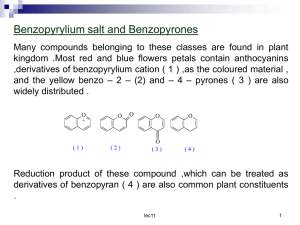
Naphtyl-imidazo-anthraquinones as novel colorimetric
... fluorophores/chromophores linked to a coordinating unit through a spacer. The coordinating unit may be tailored by a proper choice of donor functions, able to coordinate a metal ion, and the molecular framework is determined by the target metal ion. Considering colorimetric/fluorimetric sensors, a c ...
... fluorophores/chromophores linked to a coordinating unit through a spacer. The coordinating unit may be tailored by a proper choice of donor functions, able to coordinate a metal ion, and the molecular framework is determined by the target metal ion. Considering colorimetric/fluorimetric sensors, a c ...
Surface chemistry of carbon dioxide - Max-Planck
... the 2n u orbital. The six occupied orbitals may be classified as two cy-C-O bonds (3cyg,2%) and two lone pairs (4%, 3%). The lnu represents the n C - O bonds and lng the n lone pairs. In order to judge the stability of the linear geometry, Fig. 1 shows, in a qualitative way, the energy positions of ...
... the 2n u orbital. The six occupied orbitals may be classified as two cy-C-O bonds (3cyg,2%) and two lone pairs (4%, 3%). The lnu represents the n C - O bonds and lng the n lone pairs. In order to judge the stability of the linear geometry, Fig. 1 shows, in a qualitative way, the energy positions of ...
Scalable graphene field-effect sensors for specific protein detection
... the nanomaterial changes when charged molecules bind in close proximity to the material surface. Graphene, an atomically thin sheet of carbon atoms, is particularly promising as the electric-field-sensitive component of nanoFET biosensors. Graphene FETs (GFETs) on standard substrates exhibit a room ...
... the nanomaterial changes when charged molecules bind in close proximity to the material surface. Graphene, an atomically thin sheet of carbon atoms, is particularly promising as the electric-field-sensitive component of nanoFET biosensors. Graphene FETs (GFETs) on standard substrates exhibit a room ...
PDF File
... group at U(–1), despite the weaker electron-withdrawing ability of 2′-OH than 2′-F [2]. As a 2′-fluoro group contains lone-pair electrons that can accept hydrogen bonds but cannot donate hydrogen bonds, the higher reactivity of the substrate with 2′-OH than 2′-F at U(–1) suggests that hydrogen-bond ...
... group at U(–1), despite the weaker electron-withdrawing ability of 2′-OH than 2′-F [2]. As a 2′-fluoro group contains lone-pair electrons that can accept hydrogen bonds but cannot donate hydrogen bonds, the higher reactivity of the substrate with 2′-OH than 2′-F at U(–1) suggests that hydrogen-bond ...
PDF File
... and its neighbor to either side (Freier et al., 1986; Mathews et al., 1999). In 1983, concomitant with publication of a possible secondary structure for the Tetrahymena group I intron from phylogenetic comparisons (Michel and Dujon, 1983; Waring et al., 1983), Cech et al. published a secondary struc ...
... and its neighbor to either side (Freier et al., 1986; Mathews et al., 1999). In 1983, concomitant with publication of a possible secondary structure for the Tetrahymena group I intron from phylogenetic comparisons (Michel and Dujon, 1983; Waring et al., 1983), Cech et al. published a secondary struc ...
عرض تقديمي من PowerPoint
... All three membered rings have one major property in common- a strained ring which confers great reactivity on the compounds in comparison with their openchain analogues. ...
... All three membered rings have one major property in common- a strained ring which confers great reactivity on the compounds in comparison with their openchain analogues. ...
Cation–pi interaction

Cation–π interaction is a noncovalent molecular interaction between the face of an electron-rich π system (e.g. benzene, ethylene, acetylene) and an adjacent cation (e.g. Li+, Na+). This interaction is an example of noncovalent bonding between a monopole (cation) and a quadrupole (π system). Bonding energies are significant, with solution-phase values falling within the same order of magnitude as hydrogen bonds and salt bridges. Similar to these other non-covalent bonds, cation–π interactions play an important role in nature, particularly in protein structure, molecular recognition and enzyme catalysis. The effect has also been observed and put to use in synthetic systems.