Automated Detection and Classification of Intracranial Aneurysms based on 3D Surface Analysis
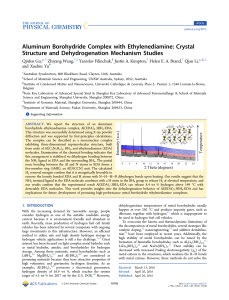
... research. The classification method resulted in a ∼20% increase in prediction accuracy, compared to other commonly used shape indexes. These results support the utility of writhe number aneurysm shape analysis as a high order descriptor with potential clinical use in intracranial aneurysm detection ...
... research. The classification method resulted in a ∼20% increase in prediction accuracy, compared to other commonly used shape indexes. These results support the utility of writhe number aneurysm shape analysis as a high order descriptor with potential clinical use in intracranial aneurysm detection ...
Chapter 3: Ionic and Covalent Compounds Chapter 3: Ionic and
... 80. Anions are formed when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons. A) True B) False Ans: A Difficulty: Easy 81. The (II) in the name of the ionic compound lead (II) acetate specifically indicates that there are two lead ions present in the compound. A) True B) False Ans: B Difficulty: Medium 82. ...
... 80. Anions are formed when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons. A) True B) False Ans: A Difficulty: Easy 81. The (II) in the name of the ionic compound lead (II) acetate specifically indicates that there are two lead ions present in the compound. A) True B) False Ans: B Difficulty: Medium 82. ...
Heterogeneous Catalysis and Solid Catalysts
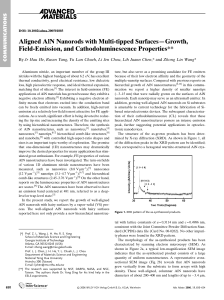
... used frequently in recent years, implying that chemical processes may be made environmentally benign by taking advantage of the possible high yields and selectivities for the target products, with little or no unwanted side products and also often high energy efficiency. The basic chemical principle ...
... used frequently in recent years, implying that chemical processes may be made environmentally benign by taking advantage of the possible high yields and selectivities for the target products, with little or no unwanted side products and also often high energy efficiency. The basic chemical principle ...
Adhesion

Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another (cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another). The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be divided into several types. The intermolecular forces responsible for the function of various kinds of stickers and sticky tape fall into the categories of chemical adhesion, dispersive adhesion, and diffusive adhesion. In addition to the cumulative magnitudes of these intermolecular forces, there are certain emergent mechanical effects that will also be discussed at the end of the article.