The Periodic Table - Harlan Independent Schools
... As you get to the bottom of the list, you will find the radioactive radium (Ra). While radium is not found around your house anymore, it used to be used in glow-in-thedark paints. The other elements are found in many items including fireworks, batteries, flashbulbs, and special alloys. The lighter a ...
... As you get to the bottom of the list, you will find the radioactive radium (Ra). While radium is not found around your house anymore, it used to be used in glow-in-thedark paints. The other elements are found in many items including fireworks, batteries, flashbulbs, and special alloys. The lighter a ...
Sections 6.4 - 6.5
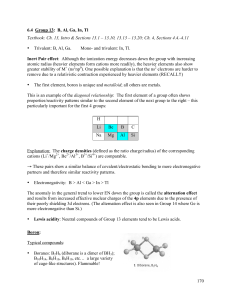
... Through the use of lead piping the Romans found out that Pb(OAc)2 tastes very sweet and used to add it to their wine. Some historians claim that this habit contributed to the collapse of their empire – they were all a little dumber than they should have been … ...
... Through the use of lead piping the Romans found out that Pb(OAc)2 tastes very sweet and used to add it to their wine. Some historians claim that this habit contributed to the collapse of their empire – they were all a little dumber than they should have been … ...
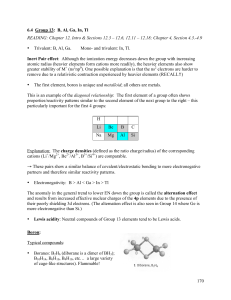
6.5 Main Group
... Through the use of lead piping the Romans found out that Pb(OAc)2 tastes very sweet and used to add it to their wine. Some historians claim that this habit contributed to the collapse of their empire – they were all a little dumber than they should have been … ...
... Through the use of lead piping the Romans found out that Pb(OAc)2 tastes very sweet and used to add it to their wine. Some historians claim that this habit contributed to the collapse of their empire – they were all a little dumber than they should have been … ...
Name - TeacherWeb
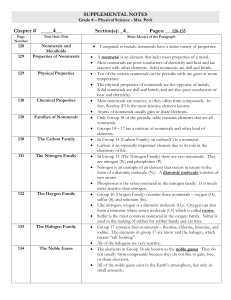
... The elements in Group 18 are known as the noble gases. They do not usually form compounds because they do not like to gain, lose, or share electrons. All of the noble gases exist in the Earth’s atmosphere, but only in small amounts. ...
... The elements in Group 18 are known as the noble gases. They do not usually form compounds because they do not like to gain, lose, or share electrons. All of the noble gases exist in the Earth’s atmosphere, but only in small amounts. ...
Chemistry Test Study Guide
... two valence electrons, many are minerals Halogens – Group 17, most reactive nonmetals, have 7 valence electrons many are used as disinfectants Noble Gases – Group 18, least reactive elements, full outer electron cloud, many are used in neon signs. Boron Family – Group 13, have 3 valence electrons Tr ...
... two valence electrons, many are minerals Halogens – Group 17, most reactive nonmetals, have 7 valence electrons many are used as disinfectants Noble Gases – Group 18, least reactive elements, full outer electron cloud, many are used in neon signs. Boron Family – Group 13, have 3 valence electrons Tr ...
chapters 1-4
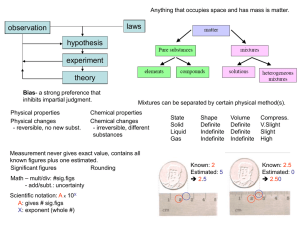
... Atom – smallest building block; molecule – combination of two or more atoms. Can be an element or compound. ...
... Atom – smallest building block; molecule – combination of two or more atoms. Can be an element or compound. ...
Study Guide Answers
... classify as either metal, nonmetal, or metalloid: Ca, Cl, I, Ir, Si, and Ti. Metals Ca-calcium Ir-iridium Ti-titanium ...
... classify as either metal, nonmetal, or metalloid: Ca, Cl, I, Ir, Si, and Ti. Metals Ca-calcium Ir-iridium Ti-titanium ...
Element Symbol
... 17. Elements are made up of one kind of atom and has a unique symbol. 18. Symbols are usually a 1 or 2 letters that stand for the name of the substance. The first letter is always capitalized and the second, if there is one, is lower case. ...
... 17. Elements are made up of one kind of atom and has a unique symbol. 18. Symbols are usually a 1 or 2 letters that stand for the name of the substance. The first letter is always capitalized and the second, if there is one, is lower case. ...
Periodic Trends
... – Ductile: drawn into a wire – Malleable: hammered into thin sheets – Good conductors of heat/electricity – Luster: shine – Solid at room temperature (except for Hg) ...
... – Ductile: drawn into a wire – Malleable: hammered into thin sheets – Good conductors of heat/electricity – Luster: shine – Solid at room temperature (except for Hg) ...
Objective 3 Stations Student Sheet
... 1. How is the periodic table organized? 2. What family of elements has valence electrons at two energy levels? 3. What are the elements called that are between metals and nonmetals? 4. Which family of nonmetals has seven valence electrons? 5. What are some properties of noble gases? 6. What is anoth ...
... 1. How is the periodic table organized? 2. What family of elements has valence electrons at two energy levels? 3. What are the elements called that are between metals and nonmetals? 4. Which family of nonmetals has seven valence electrons? 5. What are some properties of noble gases? 6. What is anoth ...
lecture_CH1-2review_chem121pikul
... • Insulators, nonconductors of electricity and heat • Chemical reactivity varies • Exist mostly as compounds rather then pure elements • Many are gases, some are solids at room temp, only Br2 is a liquid. ...
... • Insulators, nonconductors of electricity and heat • Chemical reactivity varies • Exist mostly as compounds rather then pure elements • Many are gases, some are solids at room temp, only Br2 is a liquid. ...
Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids (Vocabulary)
... are arranged by properties and are represented by one or two letter chemical symbols. ...
... are arranged by properties and are represented by one or two letter chemical symbols. ...
Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids (Vocabulary)
... Metalloids Elements which can have both properties of metals and nonmetals. Also may be called a semi-conductor. ...
... Metalloids Elements which can have both properties of metals and nonmetals. Also may be called a semi-conductor. ...