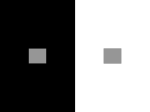* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download feature analyzers in the brain
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Response priming wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Visual extinction wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
C1 and P1 (neuroscience) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Efficient coding hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
PART 2: SENSORY WORLDS #09: FEATURE ANALYSIS IN TOADS I recognition & localization of predators & prey feature analyzers in the brain from recognition to response summary PART 2: SENSORY WORLDS #09: FEATURE ANALYSIS IN TOADS I recognition & localization of predators & prey feature analyzers in the brain from recognition to response summary FEATURE ANALYSIS IN TOADS common toad – Bufo bufo order: Anura family: Bufonidae ~ 200 toad species environment adaptable to climate prefer temperate & humid reproduction patterns ~ rainfall species-specific mate calls FEATURE ANALYSIS IN TOADS prey insects, beetles, earthworms larger toads... birds, frogs predators snakes, birds, carnivorous mammals middle of the food chain sensory: predator or prey signal ? motor: appropriate behavior opposite responses to stimuli must be fast FEATURE ANALYSIS IN TOADS interesting neuro-ethology subjects because of highly selective (not merely sensitive) visual system classify predator & prey signals appropriate behavior accessible visual system RECOGNITION & LOCALIZATION OF PREDATORS & PREY vision > auditory, olfactory, tactile senses responses triggered by movement RECOGNITION & LOCALIZATION OF PREDATORS & PREY natural environment stereotypic responses to predator & prey distinguished using aspects 4 types of response orient (o) approach (a) fixate (f) snap (s) p.97 fig.4.1 of moving stimulus prey vs non-prey natural environment FAP ? innate responses naïve animals do it... linked action patterns only o-a-f-s sequence ? sign stimuli ? releasing mechanism ? p.97 fig.4.1 RECOGNITION & LOCALIZATION OF PREDATORS & PREY RECOGNITION & LOCALIZATION OF PREDATORS & PREY p.97 fig.4.1 natural environment feature detector neuron(s) selectively responsive specific stimulus does it work this way ? RECOGNITION & LOCALIZATION OF PREDATORS & PREY natural environment not rigid linked o-a-f-s sequence different stimulus different response sequence eg: prey @ constant distance o-o-o-o-oo... (lab experiment) ~ distance & movement no behavioral prerequisites p.99 fig.4.2 RECOGNITION & LOCALIZATION OF PREDATORS & PREY natural environment possible identified features of small invert. prey elongated shape movement parallel to body axis used in lab experiments to study neural mechanisms RECOGNITION & LOCALIZATION OF PREDATORS & PREY prey-catching in the laboratory hunger motivation to attempt prey capture p.97 fig.4.1 definition... RECOGNITION & LOCALIZATION OF PREDATORS & PREY prey-catching in the laboratory glass cylinder cardboard dummy stimuli 3 “worm” types rotated 20°/s releasing value o / min direction p.99 fig.4.2 RECOGNITION & LOCALIZATION OF PREDATORS & PREY prey-catching in the laboratory optimal dummy stimulus ? shape size (s) color contrast orientation thickness composition velocity p.99 fig.4.2 RECOGNITION & LOCALIZATION OF PREDATORS & PREY prey-catching in the laboratory worm stimulus releasing value ~ s antiworm (= “amount”) releasing value ~ s square biphasic ~ s (bugs predators ?) p.100 fig.4.3 RECOGNITION & LOCALIZATION OF PREDATORS & PREY prey-catching in the laboratory worm variations releasers ? contrast orientation thickness composition direction p.101 fig.4.4 RECOGNITION & LOCALIZATION OF PREDATORS & PREY prey-catching in the laboratory worm variations releasers ? contrast orientation thickness composition direction velocity p.101 fig.4.4 RECOGNITION & LOCALIZATION OF PREDATORS & PREY prey-catching in the laboratory toads respond to shape + direction in variety of conditions invariance recognition robust informs about releasing mechanism relationship critical configural property emergent (whole > sum of parts) RECOGNITION & LOCALIZATION OF PREDATORS & PREY prey-catching in the laboratory toads respond to shape + direction response to continuum ~ threshold not single feature response ~ velocity more is better... p.101 fig.4.4 FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN toad visual system retina (vertebrates) optic nerve contralateral optic tectum thalamic pretectum (TP) (fewer projections) p.103 fig.4.5 FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN toad visual system retina (vertebrates), 5 cell types receptor cells bipolar cells in series ganglion cells horizontal cells amacrine cells FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN toad visual system retina (vertebrates), 5 cell types receptor cells bipolar cells ganglion cells horizontal cells amacrine cells FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN toad visual system retina (vertebrates), 5 cell types receptor cells: input elements, transduce light rods cones bipolar cells: relay elements ganglion cells: output brain via optic nerve lateral interactions with retina horizontal cells amacrine cells FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN toad visual system retinal ganglion cell receptive fields space that excites or inhibits neuron activity circular, 2 concentric regions center surround FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN toad visual system retinal ganglion cell receptive fields space that excites or inhibits neuron activity circular, 2 concentric regions center: excitatory (ERF) surround: inhibitory (IRF) p.104 fig.4.6 FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN toad visual system retinal ganglion cell receptive fields space that excites or inhibits neuron activity circular, 2 concentric regions center: inhibitory (IRF) surround: excitatory (ERF) p.104 fig.4.6 FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN toad visual system retinal ganglion cell receptive fields space that excites or inhibits neuron activity circular, 2 concentric regions center surround retinal ganglion cells distinguished by position (lateral axis) FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN toad visual system ganglion cells contralateral orderly maps retinotopic projections optic tectum thalamic pretectum (TP) p.105 fig.4.7 FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN toad visual system ganglion cells contralateral orderly maps retinotopic projections neuron classes R1-6 different layers optic tectum thalamic pretectum (TP) p.103 fig.4.5 FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli neurons that respond (spike) differentially ? prey recognition neurons / families of neurons ? extracellular recordings 6 neuron classes (R1 R6) early findings, center ERFs: R2: 4° R3: 8° R4: 16° no stimulus quality info... p.106 fig.4.8 FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli no classes of neurons respond ~ behavior... no response ~ long axis of stimulus no worm p.107 fig.4.9 preference antiworm ~ square FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field... eg, R3 cells p.107 fig.4.9 FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field p.107 fig.4.9 8° ERF IRF FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field p.107 fig.4.9 8° FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field p.107 fig.4.9 8° FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field p.107 fig.4.9 8° FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field p.107 fig.4.9 8° FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field p.107 fig.4.9 8° FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field p.107 fig.4.9 8° FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field p.107 fig.4.9 8° FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field p.107 fig.4.9 8° FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field p.107 fig.4.9 8° FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field p.107 fig.4.9 8° FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field p.107 fig.4.9 8° FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field p.107 fig.4.9 8° FEATURE ANALYZERS IN THE BRAIN retinal ganglion cell responses to relevant stimuli how do receptive fields ~ responses ? stimulus movement ~ receptive field... logic works p.107 fig.4.9 for R2 & R4 does not find feature analyzers in brain