* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 23mri2
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Broca's area wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
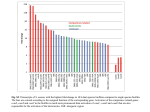
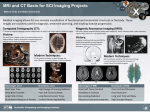
MRI - functional MRI, spectroscopy, etc Lecture 23 Functional MRI: Principles Magnetic susceptibility χ: M is the magnetization of the material, H is the strength of the external magnetic field Prerequisites: Oxyhemoglobin (oxygen rich hemoglobin) which delivers oxygen in arteries to brain cell is diamagnetic χ > 0 Deoxyhemoglobin (oxygen poor hemoglobin) which gave some of its oxygen molecules to brain cells is paramagnetic: χ <0 χdeoxy>>χoxy ratio ~ 65 Paramagnetic substance produces microscopic field inhomogeneities that decreases the transverse relaxation time T2 of the blood and surrounding tissues. T2* images and blood oxygen level depend (BOLD) contrast (Ogawa, 1990) Oxygenated blood Diamagnetic Neuron De-oxygenated blood Paramagnetic Oxyhemoglobin and Deoxyhemoglobin in Veins during Brain Activation Activation Rest Normal blood flow High blood flow Oxyhemoglobin Deoxyhemoglobin Neural activation increased demand for oxygen increased flow increased blood flow altered oxi /dioxi ratio Naively, this would lead to decrease of T2. However the blood flow overcompensates the demand so T2 actually increases in the area of the neural activity. One studies the difference between on and off task. Perspectives: Mapping of brain function in health and disease in response to various stimulation paradigm Intensity BOLD fMRI Time BOLD effect Statistical map t Task mean Re st mean s tan dard deviation activation thresholded Activation and structural image Clinical applications tumor • Mapping motor and language areas in patients with brain tumors • Neurosurgeon guided by fMRI Activation upon Perception of Disgust Faces from a standard set were computer-transformed, to create two levels of intensity of expressed fear and disgust. Examples of faces depicting 100% neutral, 75 and 150% disgust, and 75 and 150% fear are demonstrated, together with an example of a stimulus depicting a mildly happy expression (75% neutral and 25% happy) which was used as the neutral baseline. Phillips et al, Nature 389:495 (1997) Figure 1 (next slide) Generic brain activations in seven right-handed normal subjects during perception of faces depicting 75% (top row) and 150% (bottom row) disgust intensity. The grey-scale template was calculated by voxel-by-voxel averaging of the individual EPI images of all subjects, following transformation into Talairach space. The transverse sections in each experiment are at 2 mm below (left) and 9 mm above (right) the AC-PC line (right side of the brain on the left side of each section, and vice versa). Major regions of activation (probability of false activation <0.004) for perception of faces depicting 75% disgust versus a neutral expression are demonstrated in the right insula (I) and right medial frontal cortex (BA 32); those for faces depicting 150% disgust versus a neutral expression are demonstrated in the right and left anterior insula (I), right anterior insula bordering on inferior frontal cortex (BA 44), right putamen (P), and right middle temporal gyrus (BA 21). Figure 2 (next slide) The difference image demonstrating significant (P < 0.004) differences in activation for perception of faces depicting 150% intensity of disgust (versus a neutral expression) and faces depicting 75% intensity of disgust (versus a neutral expression). The grey-scale template was as for Fig. 1. The largest region of activation was in the right anterior insula (Talairach coordinates 38, 17, 9), with twice the number of activated voxels compared with other regions of the difference image. Transverse (z = 9) and coronal (y = 17) sections are shown depicting this activation in the right insula. Activation upon Perception of Disgust difference 75% 150% Phillips et al, Nature 389:495 (1997) Figure 1 (next slide) A representative axial slice from a 'late' bilingual subject (A) shows all voxels that pass the multistage statistical criteria at P < 0.0005 as either red (native language) or yellow (second acquired language). An expanded view of the pattern of activity in the region of interest (inferior frontal gyrus, Brodmann's area 44, corresponding to Broca's area) indicates separate centroids (+) of activity for the two languages. Centre-of-mass calculations indicate that the centroids are separated on this plane by 7.9 mm. The green line on the upper right midsagittal view indicates the plane location. R indicates the right side of the brain Figure 2 (next slide) A representative axial slice from an 'early' bilingual subject (G) who learned English and Turkish simultaneously during early childhood shows all voxels that pass the multistage statistical criteria at P < 0.0005. Red indicates the Turkish language task and yellow indicates the English language task. An expanded view of the region of interest (Broca's area) indicates multiple common voxels between the two language areas. The geometric centers-of-mass indicate that the centroids are within 1.5 voxels. R indicates the right side of the brain Late vs. Early Second Language Early-learned 2nd language Late-learned 2nd language Kim et al, Distinct cortical areas associated with native and second languages, Nature 388:171 (1997) QuickTime™ and a Microsoft Video 1 decompressor are needed to see this picture. Functional MR imaging of the primary motor cortex, activated when the subject’s hand repeatedly opens and closes. Note - this is NOT a real time filming. It is produced by subtraction of measurements at rest and during the activity. MR Spectroscopy (MRS) a non-invasive tool for quantitative biochemical analysis The physical basis of the MRS. Protons in lipids have slightly different resonance frequency than in water. This is because electrons in the molecule interact with external magnetic field. They have magnetic moments 1860 times larger than protons and may screen a bit the external field as their orbitals are modified by the external field. -6 where is the shielding constant expressed in units of 10 . Spectra are plotted as a function of with area under the peak proportional to the number of protons in this state. Since the shift is very small, MRS with fine tuning of the frequency to suppress signal from water. This can be done only without gradient field. Still localized measurements are possible - brain, kidneys, liver... . In addition to protons, several other nuclei are used 31P, 13C,... MRI vs. MRS With MRI you depict With MRS you determine Water; Intramyocellulae Lipids, Acetate; Alanine; Aspartate; Choline; WATER N-acetylaspartate; Creatine; myo-Inositol; Ethanol; Lactate; Glutamate; Phosphoryl-choline; and Fat Glycerophosphoryl-choline; Keton Bodies; -Aminobutyrate; Glucose; Glutamine; Glycine; scyllo-Inositol; Macromolecules; N-Acetylaspartylglutamate; O-Phosphoethanolamine; Taurine; Threonine; Glycogen; Carnosine, Carnitine, Acetylcarnitine, Phenylalanine; Succinate; Phosphocreatine; Adenosinetriphosphate; pH; NAD; 2,3Diphosphoglycerol; Deoxymyoglobin; Deoxyhemoglobin; Citrate; Betaine; Propanediol; Homo-Carnosine; Glutathione; ..... Single-Voxel MRS Studies of Alzheimer’s Disease (Neurology 2001; 57: 626-632) Single-Voxel MRS Studies of Alzheimer’s Disease Histology MRS: Evaluation of Prostate Tumors Choline 1H-MRS Creatine Choline ppm 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 Atrophy or Necrosis Citrate ppm 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 Benign Tissue Creatine Citrate ppm 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 Cancer Kurhanewicz et al, Radiology,1996; 200:489-96. MRS: Therapy Control for Prostate Tumors before Cryo-Therapy Judged by Cho/Citrate ratio successfull Cryo-therapy failed Cryo-Therapy Kurhanewicz et al Cho - choline compounds (phosphocholine, glucero-phosphocholine) Choline is a quaternary saturated amine with the chemical formula: (CH3)3N+CH2CH2OHX−. where X− is a counterion such as chloride Choline is a quaternary saturated amine with the chemical formula: (CH3)3N+CH2CH2OHX−. where X− is a counterion such as chloride A counterion is the ion that accompanies an ionic species in order to maintain electric neutrality. In table salt the sodium cation is the counterion for the chlorine anion and vice versa. In a charged transition metal complex, a simple(i.e. noncoordinated) ionic species accompanying the complex is termed the counterion. 1H MRS for Monitoring Head and Neck Cancer Response to Therapy Localization of SpectroscopicVoxel for a Patient with Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma Pre-therapy Post-therapy Proton Spectra of a Patient with Squamous Cell Carcinoma Pre-therapy Post-therapy MRI of Thin Air … but surely you can’t image air ! No, not thick air, but if we add hyperpolarized gas, …! Hyperpolarized 129 Xe Imaging Polarization is performed using a circularly polarized laser light (s+, the red wavy line in left picture) tuned to the specific transition in Rb. This causes population to build up in the 5S state of Rb. 1/2polarization to the Xe. The N A collision will have a chance to exchange this is present to keep fluorescence of the Rb to a minimum. Put all of this inside2 a weak magnet and one has polarized our xenon far greater then any magnet alone 129 Xe MRI of the lung 1 H QuickTime™ and a GIF decompressor are needed to see this picture. movie: http://imaging.med.virginia.edu/hyperpolarized/rendering.htm Volume rendering of lungs using hyperpolarized He. 3 A 3D FLASH sequence was used to obtain the 60 sections (4.33mm thickness,each). TR/TE = 5.85/2.5ms; Flip angle = 2.2 degrees; matrix = 70*128; FOV = 300*400 mm and time to acquire the entire 60 sections was 24.6 seconds. QuickTime™ and a GIF decompressor are needed to see this picture. Dynamic images of the human lung during inhalation and expiration of 3He Contrast Agent for MRI of Gene Expression Gd3+ hidden Gd3+ exposed If galactosidase is present (i.e. gene expressed), it cleaves a sugar residue to expose (activate) Gd3+, a MRI contrast agent. Schematic of the transition of EgadMe from a weak to a strong relaxivity state. In vivo visualization of gene expression using MRI Angelique Y. Louie et al. Nature Biotechnology 18,К321К-К325 (2000) EgadMe, a contrast agent, consists of chelated gadolinium caged by a galactopyranose molecule. The cage door is removed only when EgadMe comes in contact with a beta-galactosidase enzyme. (A) Schematic diagram representing the site-specific placement of the galactopyranosyl ring on the tetraazamacrocycle (side view). Upon cleavage of the sugar residue by beta beta-galactosidase (at red bond), an inner sphere coordination site of the Gd3+ ion becomes more accessible to water. (B) Space-filling molecular mode (top view, from above the sugar residue) of the complex before (left) and after cleavage by the beta-gal (right), illustrating the increased accessibility of the Gd3+ ion (magenta) upon cleavage: white, H; red, O; blue, N; gray, C.