* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Case Study 71
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmune encephalitis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis signs and symptoms wikipedia , lookup
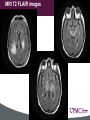
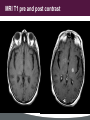
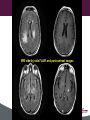
Clayton Wiley MD/PhD 38-year-old male with progressive weakness of upper and lower extremities, in addition to confusion. Describe the MRI findings (location, enhancement, mass effect). MRI T2 FLAIR images MRI T1 pre and post contrast MRI side-by-side FLAIR and postcontrast images Question 1 What additional clinical information would you like to know? Answer Is there any significant past medical history? signs/symptoms of infection previous malignancy (Fam Hx) Previous treatments PE- evidence of peripheral lesions or infections? Lab- Blood and CSF analysis Question 2 Give a differential diagnosis based on MRI. Answer • Infectious disease (Toxoplasmosis, Amebic encephalitis, Viral, PML) • Lymphoma • Demyelinating lesion (Multiple sclerosis) • Metastasis • Gliomatosis cerebri • Multiple infarcts (Embolic / Vasculopathy) Question 3 The surgeon tells you that a full body CT showed no masses, an HIV test was positive and the CSF showed lymphocytes. You receive 2 cores of tissue in consultation for intraoperative guidance. Describe the cytologic features of the touch prep and smear. Click here to view slides. Question 4 What is your intraoperative diagnosis? Question 5 What can a neuropathologist do to validate their diagnosis? Answer LCA, CD20/L26 & CD3. Other hematopoietic markers (ie CD79a, kappa, lambda, CD10, MUM-1, etc) and vimentin/GFAP (to highlight gliosis) might also be helpful in certain cases. Question 6 Review the permanent section and describe the microscopic features. Click here to view slide. Question 7 What is your final diagnosis? Question 8 Secondary involvement by lymphoma is most common in what part of the CNS? Answer Dura / leptomeninges Question 9 What are some diseases associated with PCNSL? Answer • • • • • HIV infection Immunosuppressive therapy (post transplantation) Hodgkin's disease Epstein-Barr virus Primary immunodeficiency syndromes: Wiskott-Aldrich, Xlinked lymphoproliferative, Severe combined immunodeficiency, Ataxia-telangiectasia