* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Engineering - ABC-MissAngelochsBiologyClass
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
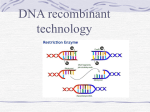
Genetic Engineering How is this possible? Jelly Fish Gene Mice Recombinant DNA Technology Connecting fragments of DNA from different sources Transgenic Organisms Plants and animals that contain fragments of DNA from different sources. Example: tobacco plant with firefly gene that makes the plant glow Bacteria and Recombinant DNA Technology Scientists commonly use bacteria to produce substances like human insulin or human growth hormone They all use bacteria because they reproduce asexually and reproduce rapidly Creating Bacteria with Human Genes (DNA) – Step 1 Cut a piece of DNA that codes for a specific gene using restriction enzymes (act like scissors). They cut DNA at a specific nucleotide sequence. Example: Step 2 Cut plasmid (small circular DNA found in bacteria) with restriction enzymes. Step 3 Gene splicing: Foreign DNA is attached to the plasmid creating recombinant DNA. The recombinant DNA is inserted into the bacteria. The bacteria will reproduce asexually. Animation http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x2jUM G2E-ic http://www.dnai.org/text/mediashowcase/ index2.html?id=549 Recombinant DNA Technology What do scientists use this for? To produce insulin, human growth hormone, enzymes to break down pollutants, produce natural insecticides, etc. The quest for the perfect tomato…. What would arctic fish have to do with making the perfect tomato? Transgenic Plants Genetically engineered plants with recombinant DNA. Example – tomato with the antifreeze gene from fish Transgenic Animals Genetically engineered animals with recombinant DNA. Ex – Creating animals with human organs for transplants Gene Therapy Inserting normal genes into human cells to correct genetic disorders Selective Breeding Choosing animals and plants to mate with desirable traits. Ex – Texas cattle and Brahman cattle What are they? Hybridization Mating individuals not closely related to introduce new beneficial genes into a population Ex – Horse (obedient) + donkey (strong) = mule (obedient and strong) Inbreeding Mating between closely related individuals to maintain desirable traits. Choosing a Mutation Seedless oranges, ancon sheep (short legged). We choose to breed mutations for our benefit. Cloning Cloning Creating identical individuals with the desired traits. Ex – Dolly the sheep, vegetative propagation, etc. Cloning Pros and Cons Pros Cons -Study -Messing and fight diseases -Clone organisms with better traits (better meat, milk, etc.) with nature -Cloning humans -Change an ecosystem – bring back organisms that are extinct -Clones live shorter lives because the DNA is aged