* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Whole genome shotgun sequencing
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA barcoding wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
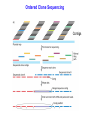
Sickle-cell anemia Caused by single bp substitution in b-globin gene Determine b-globin genotype by RFLP analysis Other methods to diagnose genotypes Allele-specific Oligonucleotides (ASOs): Make two oligonucleotide probes: (a) Normal sequence (b) Sequence of mutant allele Hybridize each oligo (separately) to Southern blot of DNA. Use conditions that allow only oligonucleotides that are 100% complementary to DNA on blot to hybridize. If only normal oligo hybridizes---homozygous normal allele If only mutant oligo hybridizes --- homozygous mutant allele If both oligos hybridize --- heterozygous Screen DNA by PCR: Similar to ASOs, in combination with a 2nd primer, use: (a) PCR primer with normal sequence (b) PCR primer with mutant sequence Will only get PCR product if the primer perfectly matches the genomic DNA. Amplify gene region by PCR & sequence it. Most of the mutations responsible for other genetic diseases do not change a restriction site (i.e., not detectable as RFLP or SSLP) Multiple mutant alleles for many of these genes. Therefore, unless you know the specific allele an individual might carry, would need to do multiple tests with different allele-specific oligos. Or -- Can detect ~all mutant alleles by sequencing. Genome Projects 1. Determine DNA sequence of entire genome. 2. Map the locations and structures of all genes (annotation). 1. Determine DNA sequence of entire genome. Two Alternative Approaches - Ordered clone sequencing: Assemble physical map = set of overlapping clones. Choose smallest number of clones needed to cover entire genome. Sequence just these clones. - Whole genome shotgun sequencing: Randomly select many clones. Determine their sequences. Use computers to align sequences. Ordered Clone Sequencing Assemble Physical Map: 1. Select random BAC clones and sequence ends of inserts. Each of these sequences = Sequence-Tagged Site (STS). 2. Design PCR primers from within these STS’s & test other BAC clones for inclusion of this DNA sequence by PCR. 3. Assemble clones into “contigs”. Contigs = set of overlapping clones. Ordered Clone Sequencing Contigs Whole genome shotgun sequencing Random clones selected and sequenced - each insert only a few kb. STS#1 STS#2 BAC clone Can use STS’s from ordered clones to help fill gaps in sequence. Virtual Cloning Do computer searches of genome databases to identify genes with similar sequences