* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
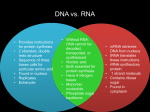
Transcription and Translation: From DNA to Proteins How can DNA code for how I look? How does this code give me black hair & brown eyes? How can this code make me tall or short? Recall: Chromosomes, Genes, and DNA •DNA makes up GENES, which are found on CHROMOSOMES. •Gene— a segment of DNA that provides information for making a specific protein. DNA is expressed as PROTEINS—determines your traits! DNA RNA Proteins (Transcription) (Translation) THE CENTRAL DOGMA! Replication DNA can’t fit through nuclear membrane, so it needs to send a “messenger” RNA (mRNA) to the ribosomes to make proteins. DNA is very important and must be kept protected! DNA Transcription RNA Nucleus Translation Protein Cytoplasm Transcription (DNA mRNA) Transcription occurs in the NUCLEUS RNA = Ribonucleic Acid (a nucleic acid) DNA is template for RNA mRNA is made of same bases, except uses URACIL instead of thymine. A pairs with U G pairs with C Every 3 letters of mRNA are called a CODON. Transcription The new mRNA molecule is formed by incorporating nucleotides that are complementary to the template strand. DNA coding strand 5 ’ 3’ DNA GT CA TT CGG 3’ G UC AUUCG G 3’ C AG T AAGCC 5’ DNA template strand 5 ’ RNA DNA vs. RNA RNA DNA 1. Single-stranded 1. Double-stranded 2. A pairs with Uracil (U) 2. A pairs with Thymine (T) 3. Sugar = Ribose 3. Sugar = Deoxyribose 4. Location = Nucleus and Ribosomes 4. Location = Nucleus There are 3 Types of RNA mRNA Messenger Job is to carry the message from the nucleus to the ribosome tRNA Transfer Job is to transfer the amino acids to the ribosome Only in cytoplasm •rRNA •Ribosomal •Composes the ribosome itself •Only in cytoplasm Three types of RNA Translation (mRNA Protein) Takes place in RIBOSOMES mRNA is template for tRNA Transfer RNA (tRNA) tRNA translates the message, picks up corresponding amino acid, and puts it together into a protein chain. Every 3 letters of tRNA are called an ANTICODON. Translation DNA mRNA tRNA DNA mRNA tRNA ATC CTA GTG CAT UAG GAU CAC GUA AUC CUA GUG CAU Amino Acids—make up proteins "Why do we need mRNA if DNA holds all the genetic instructions for the proteins the cell needs to produce?" DNA must be protected at all costs AND it is too big to leave the nucleus. Vocabulary to Know…. DNA Nucleus Ribosomes Transcription Translation RNA Protein mRNA tRNA Amino acid Quiz yourself!!!!!!