* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell transport ppt. - student notes
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
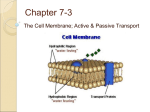
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell Transport There are TWO types of cell transport: 1) Passive transport- NO ENERGY required. 2) Active transport- ENERGY required. Passive Transport In passive transport, substances move across the cell membrane WITH the concentration gradient. Substances move from HIGH to LOW concentrations. High concentration of substances Low Concentration This is ALSO known as DIFFUSION. Simple _________= The movement of molecules from high concentrations to low concentrations. ________= the diffusion of WATER. Concentration gradient= _________________________________________________ (must exist in order for molecules to flow). Brownian movement Molecules are able to naturally diffuse due to a mechanism called _________ movement- the random _____________________. Particles suspended in a gas or a liquid are bombarded by fast moving atoms or molecules. There are THREE types of passive transport: 1) 2) 3) Osmosis _____________________ ____________ Osmosis Osmosis is diffusion of _____. Which of the diagrams at right best represents the movement of molecules in osmosis? A, B, C or D? Cell Environments Too much water in the cell= __________ Cell will _____ if environment remains hypotonic; percentage of water is higher outside the cell than in. Too little water in cell= __________ Cell will ______ if it is exposed to a hypertonic environment; percentage of water is lower outside the cell than in. Cell environment where concentrations of water are equal inside and outside the cell= _________(ideal) Hypertonic A cell is in a hypertonic solution if the concentration of _______________________________ than the concentration outside the cell. Water diffuses from high to low. Water _______________. This is why you should NEVER drink salt water. Doing so will severely _________ you! Think “SALT SUCKS” Hypotonic A cell is in a hypotonic solution if the concentration of _________________________________ than the concentration outside the cell. Water diffuses from ___________. Water _____________________. Isotonic Water concentration stays _____ inside and outside the cell. Water enters and leaves the cell at equal rates. ________________________. Facilitated Diffusion The passive transport of materials across the cell membrane with the aid of _________; a common method of moving ______ and ___________. Ion channels Special transport proteins with _________ that can open and close. Allow ______in and out of the cell (examples of ions= _____,_____,_____). Let’s review __________ transport does NOT require energy. Active transport DOES require ___________. During passive transport, substances move from _______ to ______ concentrations. ____________ is the diffusion of water. _________________ solutions could cause a cell to burst. Facilitated diffusion uses proteins to allow ___________ and amino acids into or out of the cell. Ion channels are proteins with special __________ that can open or close to let _______ in or out. Active Transport Active transport moves substances across the cell membrane AGAINST the concentration gradient (energy needed to do so). Substances move from LOW to HIGH concentrations. (Opposite of passive transport). Examples of Active Transport 1) Exocytosis 2) Sodium-Potassium Pump Endocytosis Recall that active transport requires energy (ATP). Molecules that are actively transported go AGAINST the concentration gradient (or “uphill”). Endocytosis A process in which cells surround and engulf substances that are TOO BIG to enter the cell. The cell uses its own membrane to engulf the substance into a vesicle and bring it in. Exocytosis Opposite endocytosis. When a cell forms a vesicle around unwanted particles and expels it OUT of the cell. Endocytosis vs. Exocytosis *Endo means “in”; Exo means “out”. *Cyto means cell (Endocytosis= in cell; Exocytosis= out of cell) The Cell Membrane Functions) 1)The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell. 2)The cell membrane provides protection and support for the cell. 3) Communicate with other cells. The cell membrane acts as a BARRIER, separating the cell’s inside from its outside. The cell membrane is also known as the plasma membrane, and is often referred to as the semi-permeable membrane. Semi-permeable refers to the tendency for the cell to allow some materials in, but not all (like a screen or a net).