* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE CELL
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
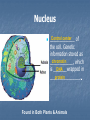
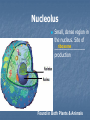
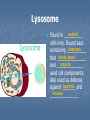
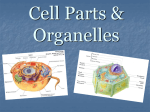
THE CELL pp. 174-181 Cell Boundaries A. Cell Wall Cell walls are the outermost boundary in bacteria plants fungi __________, _______, and ___________. animal cells They are not found in _____________________. The primary function of the cell wall is to provide ___________________________. The cell wall structure and support does not regulate what enters and leaves _________________________ the cell. 1. Cell walls of plants are composed of cellulose ____________ 2. Cell walls of fungi are composed of Chitin _____________ B. Cell Membrane B. Cell Membrane Every cell is surrounded by a cell Lipid bilayer membrane made of ___________________. The cell membrane is selectively permeable which means _____________________________________ it only allows certain substances in and certain substances out _____________________________________ __. This characteristic is critical in helping homeostasis the cell maintain _______________. The cell membrane is also called the plasma ____________________ membrane. Inside a Eukaryotic Cell The inside of the cell consists of the: A. Nucleus cytosol B. B. Cytoplasm – Includes the _________ organelles or “cell gel” and the __________, which little organs means “_____________” Nucleus Control center of _____________ the cell. Genetic information stored as chromatin ____________, which DNA is _______wrapped in ________________. protein Found in Both Plants & Animals Nucleolus Small, dense region in the nucleus. Site of ribosome ________________ production Found in Both Plants & Animals Nuclear Envelope Double phospholipid _________________ membrane. Has pores nuclear ___________ RNA which allow _______ to leave the nucleus Found in Both Plants & Animals Ribosomes Tiny, granular organelles located on Endoplasmic Reticulum _________________ or suspended in cytosol _________. Site of protein production _________________. All cells (pro & euk) have ribosomes. Found in Both Plants & Animals Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Extensive network continuous nuclear envelope with _________________. Called “rough” because it has ribosomes ________________ all along the membrane. Function of the rough ER is to modify & transport proteins _____________________. Most of these proteins are vesicles packaged into _____________ (like bubbles or sacs) and Golgi apparatus shuttled to the ____________ Found in Both Plants & Animals Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Similar to rough ER in structure, except that it lacks ribosomes ______________. The smooth ER manufactures lipids ________, breaks glycogen down _________, detoxifies poisons __________, and stores calcium ________________. Found in Both Plants & Animals Golgi Apparatus Flattened, round sacs that look like a sack pancakes of ________________. Receives, modifies, and ships products by way of ___________ vesicles cytosol → cell membrane_ into the ____________________________ Found in Both Plants & Animals Lysosome animal Found in __________ cells only. Round sacs enzymes containing __________ break down that _______________ recycle and ______________ used cell components. Also used as defense bacteria and against _______ viruses _______________ Vacuole Sacs that may be used as storage for _______, _________, water Salts, proteins carbohydrates _________________, or wastes. Plants have a large central vacuole. Mitochondria Double-walled organelle with inner to increase folds ____________. surface area ____________Uses glucose to _______ manufacture energy in the form of ATP ______. Mitochondria have their own DNA _______. Chloroplast plant Found in ______ cells. Contain chlorophyll (green __________ pigment) and their DNA own ______. Chloroplasts harvest sun energy from the ____ to produce ATP ____ through photosynthesis __________. Centrioles animal Found in _________ cells only. Bundles of _________________ microtubules that play a role in cell division _________________ Cytoskeleton microtubules Composed of protein fibers known as _______________ and ______________. and microfilaments Anchor _______________ organelles provide ______________. Also provide motility for some structure cilia flagella cells in the form of ___________ or ____________. More animal extensive cytoskeleton found in __________ cells.