* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Discovery
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
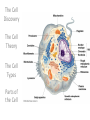
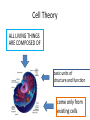
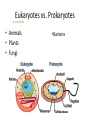
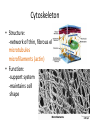
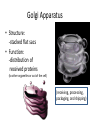
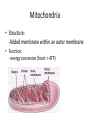
CELL STRUCTURE Jan Homolak, 2nd year School of Medicine, Zagreb 4/28/2014 Mentor: A. Žmegač Horvat The Cell Discovery The Cell Theory The Cell Types Parts of the Cell Cella = small room Cell Discovery Robert Hooke - observed a thin slice of cork (dead plant cells) Microphagia - described what he observed as “little boxes” (cells) 1665 Anton van Leeuwenhoek first person to observe living cells 1675 Cell Theory ALL LIVING THINGS ARE COMPOSED OF basic units of structure and function come only from existing cells Matthias Schleiden (1838) -all plants are composed of cells Theodor Schwann (1839) - all animals are composed of cells Rudolph Virchow (1855) - cells come only from other cells ??? • The largest cell in the human body? the female ovum • The smallest cell in the human body? male sperm (175,000 sperm cells weigh as much as a single egg cell) • The largest cell on earth? an ostrich egg • The smallest cell? a tiny bacteria • which cell is the most abundant in the human body? There are more bacterial cells in the body than human cells. Eukaryotes vs. Prokaryotes true nucleus • Animals • Plants • Fungi •Bacteria Prokaryotes Eukaryotes nucleus? NO (nucleoid) YES membrane-bound organelles? NO YES (Many) size 1 - 10 m 10 - 50 m when evolved? 3.5 billion years ago 1.5 billion years ago cytoplasm? YES YES cell membrane? YES YES cell wall? Some Do Plants ribosomes? YES YES DNA? Circular Free Floating Chromosomes in Nucleus examples Bacteria Plants, Animals, Fungi, and Protists Parts of the Cell • • • • taking food transforming food into energy getting rid of wastes reproducing Cell Membrane • Structure: - phospholipid bilayer - proteins: - channels - markers - receptors • Function: “selectively permeable boundary between the cell and the external environment” Nucleus • Structure: a sphere • Function: -storage center of cell DNA -manages cell functions Cytoplasm • Structure: - gelatin-like fluid - inside the cell membrane • Function: -contains salts, minerals, and organic molecules -surrounds the organelles Cytoskeleton • Structure: -network of thin, fibrous elements microtubules microfilaments (actin) • Function: -support system -maintains cell shape Ribosomes • Structure: -two subunits made of protein and RNA • Function: -protein synthesis Endoplasmic Reticulum • Structure: -a system of membranous tubules and sacs • Function: -”intercellular highway” rough endoplasmic reticulum smooth endoplasmic reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • Covered with ribosomes • Protein synthesis and export Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum • Synthesis of lipids and breakdown of toxic substances Golgi Apparatus • Structure: -stacked flat sacs • Function: -distribution of received proteins (to other organelles or out of the cell) (receiving, processing, packaging, and shipping) Mitochondria • Structure: -folded membrane within an outer membrane • Function: - energy conversion (food -> ATP) Lysosomes • Structure: -spherical organelles • Function: -contain hydrolytic enzymes Peroxisomes • Structure: -spherical organelles • Function: -degrade hydrogen peroxide (toxic metabolic compound) Centrioles • Structure: -nine sets of triplet microtubules -arranged in a ring • Function: -cell division (mitosis)