* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Looking Inside Cells
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
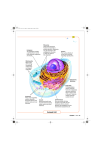
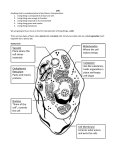
Looking Inside Cells: Organelles What Am I? Chloroplast Mitochondria Cytoplasm Cell membrane Endoplasmic reticulum Nucleus Vacuole Golgi Body Cell Wall Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum CELL WALL • A rigid layer of nonliving material that helps to protect and support the cell. VACUOLE • This sac stores water, food, waste products, and other materials. NUCLEUS • Directs all of the cell’s activities, including reproduction. CYTOPLASM • The gel-like fluid inside a cell. MITOCHONDRIA • Most of the cell’s energy is produced within these rod-shaped organelles. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM • This network of passageways carries materials from one part of the cell to another. GOLGI BODIES • These organelles receive materials from the ER and send them to other parts or outside of the cell. CELL MEMBRANE • Forms the outside boundary that separates a cell from its environment and controls what substances come into and out of a cell. CHLOROPLASTS • These organelles capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell. LYSOSOMES • These small organelles contain chemicals that break down food particles and worn-out cell parts. RIBOSOMES • These small structures function as factories to produce proteins. Edible Cell Model: Expectations • You MUST wear gloves when handling food. • Do NOT eat anything unless instructed to do so. • Misbehavior will result in your model being taken away.