* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell City: A Role Play December 14, 2006
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
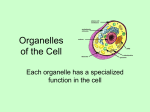
The Cell City: A Role Play Mrs. Adorno Do Now: Why do you think these cells look so different from one another? http://www.teachersdomain.org/resources/tdc02/sci/life/cell/cellgallery/index.html Form and Function… Form and Function… …go hand in hand. The cell is an example of form and function working together. The pictures show the variety of forms (shapes) cells can take and how many different jobs they perform in the human body and in other forms of life. What is so special about animal cells and their organelles? The cell is the basic unit of life. Every organism is either made up of large interconnected groups of cells or is itself a cell, free-floating and independent. There is a nearly endless variety of cell types. The human body alone contains more than 200 different kinds of cells that vary in size, shape, and function! Animal cells of different types vary widely, but one common thing is that they all have organelles that are important for their survival. Task #1: Organelle Research Your job is to work with your Group to read and answer questions. Each group will be responsible for completing the research so that you can present your findings to the class. Animal Cell Organelles Cell Membrane: The Security System of a Cell Main Jobs: The cell membrane is a barrier that keeps the contents of the cell, the cytoplasm, contained. It helps to control what materials go into and out of the cell. The CM also maintains cell shape. Talks to other cells by making cell junctions. Fun Facts: The membrane is a bilayer. What this means is that, under a strong microscope two separate layers can be seen. Cell shape. Talks to other cells Cell Membrane Animal Cell Organelles Cytoskeleton: The Road System of the Cell Main Job: The cytoskeleton gives a cell shape so that its organelles can move about and perform their duties properly. Fun Facts: When you think of the cytoskeleton, think of pillars of a building. Pillars provide a building with support so that it remains standing. The cytoskeleton also helps cells to move. The Golgi, vacuoles, and lysosomes rely upon the cytoskeleton to move. Cell shape. Talks to other cells Gives cell its shape. Holds and moves organelles. Cell Membrane Cytoskeleton Animal Cell Organelles Nucleus: The Control Center Main Job: The nucleus is a cell’s “brain.” It controls all cell activity. Factoids: The nucleus is usually round and is the largest organelle in the cell. The nucleus has three main parts: the Nucleolus, the Chromatin, and the Nuclear Envelope. Animal cells will die if their nucleus is removed. Cell shape. Talks to other cells Gives cell its shape. Holds and moves organelles. Cell Membrane Cytoskeleton Animal Cell Organelles Nucleus Controls the cell’s activities. Mitochondria Main Job: To give “power” to the cell’s other organelles. Mitochondria can be compared to a powerhouse! Fun Fact(s): Organisms get energy from a molecule called ATP. The mitochondria use food and oxygen to produce ATP to be used by the cell’s organelles. The mitochondria have their own DNA and ribosomes. Because of this, scientists believe that mitochondria used to be independently living bacteria that began living within other cells. Cell shape. Talks to other cells Gives cell its shape. Holds and moves organelles. Cell Membrane Cytoskeleton Animal Controls the cell’s activities. Nucleus Makes energy for Cell Organelles cell’s activities. Mitochondria Endoplasmic Reticulum Main Job: To transport proteins and other cellular materials to regions of the cell where they are needed. ER can be compared to the postal service! Fun Fact(s): There are two different types of ER – rough ER and smooth ER Rough ER is involved in making proteins Smooth ER makes produces other important materials such as fats. Cell shape. Talks to other cells Gives cell its shape. Holds and moves organelles. Cell Membrane Cytoskeleton Controls the cell’s activities. Nucleus Animal Makes energy for Cell cell’s activities. Organelles Mitochondria ER Transports proteins around the cell. Golgi Apparatus Main Job: To package material to be transported out of the cell. Golgi can be compared to a shipping department! Fun Fact(s): The Golgi is made up of stacks of pouches that look like pancakes. The Golgi is often called the “shipping department” of the cell. The Golgi got its name from scientist Camillo Golgi who discovered this organelle. Cell shape. Talks to other cells. Gives cell its shape. Holds and moves organelles. Cell Membrane Cytoskeleton Controls the cell’s activities. Nucleus Animal Makes energy for Cell cell’s activities. Organelles Packages materials for export from the cell. Golgi Mitochondria ER Transports proteins around the cell. Vacuole Main Job: To store proteins and cellular waste. Vacuoles can be compared to storage units! Fun Fact(s): Vacuoles in animal cells are much smaller than in plant cells. Vacuoles in animal cells can contain food that must be digested. A lysosome fuses with a vacuole and squirts digestive enzymes into the vacuole in order for the food to be broken down. Cell shape. Talks to other cells. Gives cell its shape. Holds and moves organelles. Cell Membrane Cytoskeleton Makes energy for Cell cell’s activities. Organelles Vacuole Packages materials for export from the cell. Nucleus Animal Stores materials to be used or destroyed later. Controls the cell’s activities. Golgi Mitochondria ER Transports proteins around the cell. Lysosome Main Job: To digest or break down materials. Lysosomes can be compared to “clean-up crews.” Fun Fact(s): Often cells need to tear down parts of themselves and rebuild to do their jobs. Lysosomes do this “tearing down” by digesting cell parts. For example, a tadpole loses its tail when it becomes a frog. Lysosomes digest the tail cells; the digested material from the tail is then used by the frog to build its new legs. Cell shape. Talks to other cells. Gives cell its shape. Holds and moves organelles. Cell Membrane Digests and recycles cellular waste and food. Cytoskeleton Lysosome Makes energy for Cell cell’s activities. Organelles Vacuole Packages materials for export from the cell. Nucleus Animal Stores materials to be used or destroyed later. Controls the cell’s activities. Golgi Mitochondria ER Transports proteins around the cell. Ribosome Main Job: To build proteins. Ribosomes can be called the “letter writers” of the cell. Fun Fact(s): Some ribosomes are found floating in the cell’s fluid. These are called free ribosomes. Some ribosomes are also found attached to ER. These are called bound ribosomes. A ribosomes can make the average protein in about one minute. Cell shape. Talks to other cells. Makes proteins. Gives cell its shape. Holds and moves organelles. Cell Membrane Digests and recycles cellular waste and food. Ribosome Lysosome Controls the cell’s activities. Nucleus Animal Stores materials to be used or destroyed later. Makes energy for Cell cell’s activities. Organelles Vacuole Packages materials for export from the cell. Cytoskeleton Golgi Mitochondria ER Transports proteins around the cell. What is a protein? Proteins are large molecules that build essential pieces of our bodies. They much make up about 15% of the mass of the average person. Structures in our bodies that are made of proteins: Muscles Ligaments Skin Hair Antibodies Hemoglobin The protein in the food we eat is our main source of the chemical building blocks we need to build our own protein molecules. http://www.schoolscience.co.uk/content/5/chemistry/proteins/Protch1pg1.html Cell shape. Talks to other cells. Makes proteins. Gives cell its shape. Holds and moves organelles. Cell Membrane Digests and recycles cellular waste and food. Ribosome Lysosome Controls the cell’s activities. Nucleus Animal Stores materials to be used or destroyed later. Makes energy for Cell cell’s activities. Organelles Vacuole Packages materials for export from the cell. Cytoskeleton Golgi Mitochondria ER Transports proteins around the cell. …out the… Describe what would happen to a cell if a UV ray hit the cell and destroyed the nucleus.