* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organelles of the Plant Cell - University of Central Oklahoma
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
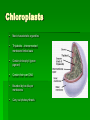
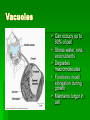
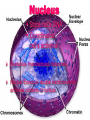
Organelles of the Plant Cell By: Valerie Gutierrez Plasma Membrane Consists of a phospholipid bilayer Controls molecules movement in and out of the cell Cell to cell signaling Cell adhesion Cell Wall Composed primarily of cellulose Provides structural support Structure of Cellulose Thomas A. NEWTON Mitochondria Powerhouse of the cell Main site of ATP production Consists of an inner membrane and an outer membrane Cristae - foldings in the inner membrane Matrix – central space Intermembrane space – space between the membranes Contain their own DNA Chloroplasts Most characteristic organelles Thylakoids – interconnected membrane-limited sacs Contain chlorophyll (green pigment) Contain their own DNA Bounded by two bilayer membranes Carry out photosynthesis Vacuoles Can occupy up to 80% of cell Stores water, ions, and nutrients Degrades macromolecules Functions in cell elongation during growth Maintains turgor in cell Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth ER Lacks ribosomes Synthesizes fatty acids and phospholipids Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum No ribosomes Rough ER Do not lack ribosomes Synthesizes, processes, and sorts secreted proteins Golgi Complex Series of flattened membrane sacs Cis and trans side Processes, sorts, and ships proteins to where they need to go “Post Office” Trans Cis Nucleus Store cell’s DNA Coordinates cell’s activities Nucleolus- manufactures ribosomes Nuclear Envelope- double membrane that encloses contents of nucleus References Kimball, John W. (2000, November). Kimball’s Biology Pages. Retrieved September 23, 2003, from http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/P/PlantCell.html Carpi, Anthony. (1998-1999). The Cell. Retrieved September 23, 2003, from http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/13-cells.htm Plant Cell Organelles. (1994-2003). Retrieved September 23, 2003, from http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/plntcell.htm Plant Cell Anatomy. (2001-2003). Retrieved September 23, 2003, from http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/plants/cell/ Lodish, Berk, Matsudaira, Kaiser, Krieger, Scott, Zipursky, Darnell. (2003). Molecular Cell Biology. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company.