* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Function of Cell Organelles
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
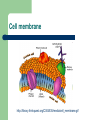
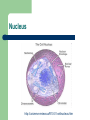
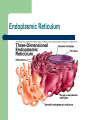
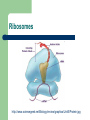
Function of Cell Organelles Function of Cell Organelles Each cell organelle has a different function All organelles within a cell work together to ensure that the cell functions properly A cell can be thought of a factory as it produces chemicals and proteins needed by the body Cell membrane http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/media/cell_membrane.gif Cell membrane The cell membrane is a ‘selective barrier’ which allows certain substances to pass through and prevents others from entering the cell Found in both plant and animal cells Nucleus http://universe-review.ca/R10-01-cellnucleus.htm Nucleus The nucleus contains the genetic material of the cell called DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). DNA is essential for the cell to function as it contains all the instructions for the cell. Nucleolus is found within the nucleus and contains RNA (ribonucleic acid). It is responsible for the production of ribosomes. Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) A network of flattened membranes used mainly for the transport of proteins Rough – ribosomes attached to the surface giving a ‘rough’ appearance. It folds and processes proteins Smooth – No ribosomes present and synthesises lipids for membranes Ribosomes http://www.sciencegeek.net/Biology/review/graphics/Unit5/Protein.jpg Ribosomes Responsible for protein synthesis necessary for the cell to function Can be found free in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER Golgi Bodies Golgi Bodies A network of membranes that are curved and stacked in groups of 4-10 The function is to process, package and sort cell products. Vesicles can be seen budding off as proteins continue on to their final destination which can be located inside or outside the cell Lysosomes http://www.cartage.org.lb/en/themes/sciences/zoology/AnimalPhysiology/Anatomy/AnimalCellStructure/Lysosomes/Lysosomes.htm Lysosome Sacs filled with digestive enzymes They break down worn out cell organelles so that the materials can be recycled to make new organelles Mitochondria http://www.chelationtherapyonline.com/anatomy/images/mitochondria.jpg Mitochondria The ‘powerhouses’ of the cell Responsible for producing ATP, an energy molecule, so cell processes can be carried out Chloroplast http://www.dnr.sc.gov/ael/personals/pjpb/lecture/chloroplast.jpg Chloroplast Organelles found only in plant cells that contain the green pigment chlorophyll They carry out the process of photosynthesis. This process requires carbon dioxide, water and sunlight to produce energy (mainly sugars) for the cell