* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NeuroMuscular Junction and Excitation Coupling IP
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
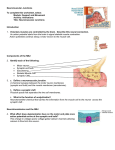
Name: ______________________________________________________ Period: __________ Partner/s: ___________________________________________________ Date: ___________ Interactive Physiology-Neuromuscular Junction Use interactive physiology and textbook pages 288-293 to complete the following. Label this diagram with these terms: axon terminal, synaptic vesicles, synaptic cleft(gap), motor end plate, T-tubule, sarcolemma, sarcomere, terminal cisternae and sarcoplasmic reticulum Study Questions on the Neuromuscular Junction: 1. (P 1.) What stimulates skeletal muscle cells to contract? ____________________________ __________________ 2. (P 1.) The place where a motor neuron stimulates a muscle cell is called a ______________________________ ______________________________ 3. (P 3.) How are skeletal muscle cells electrically insulated from each other? _______________________________ 4. (P 3.) What is a motor neuron? 5. (P3.) What part of the motor neuron carries impulses to the muscle? Describe its structure. 6. (P 4.) Match the following terms to their description: Axon terminal, Synaptic Vesicles, Synaptic Cleft Motor End Plate, T Tubule, Sarcolemma, Terminal Cisternae& Sarcoplasmic Reticulum, Sarcomere ________________ a. Invaginations of the sarcolemma penetrating deep into the interior of the muscle cell. ________________ b. The space between the axon terminal and the motor end plate. ________________ c. The swollen distal end of the motor neuron axon. ________________ d. The muscle cell membrane. ________________ e. Structures within the axon terminal that contain the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. _______________ f. The contractile unit of the muscle cell that extends from one Z line to the next. _______________ g. Structures within skeletal muscle cells that serve as reservoirs of calcium ions. ________________ h. A folded region of the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction. 7. (P 5.) What is a polarized membrane? 8. (P 5.) Describe the resting membrane potential at the neuromuscular junction? (where is the polarization and what is positive and what is negative) 9. (P 5.) Describe the T Tubules when they are at resting membrane potential. 10. (P 5.) List the following events in the order they occur: _____ a. The motor end plate is depolarized. _____ b. The sarcomeres contract. _____ c. Acetylcholine is released from the axon terminal into the synaptic cleft. _____ d. The depolarization triggers an action potential which propagates along the sarcolemma and the T tubules. _____ e. An action potential arrives at the axon terminal 11. (P6.) What happens at the neuromuscular junction when the action potential arrives at the axon terminal. 12. (P 7.) What is the effect of the presence of calcium ions inside the axon terminal? 13. (P 8.) What two events happen after the synaptic vesicles fuse with the membrane of the axon terminal? 1) 2) 14. (P 9.) What happens to acetylcholine after it is released into the synaptic cleft? 15. (P 9.) What happens after the acetylcholine binds to the acetylcholine receptor on the motor end plate? 16. (P10.) When does the chemically gated ion channel on the motor end plate close? 17. (P10.) What happens to the acetylcholine after it diffuses away from its receptor on the motor end plate? 18. (P11.) The movement of the sodium ions through the chemically gated ion channel initiates a depolarization of the motor end plate. What happens after this depolarization is generated? 19. (P12.) What happens as the action potential moves down the T Tubules? 20. (P13.) What happens when calcium ions are present in the cytosol of the muscle cell? Summary • Each skeletal muscle cell is individually stimulated by a motor neuron. • The neuromuscular junction is the place where the terminal portion of a motor neuron axon meets a muscle cell membrane, separated by a synaptic cleft. • An action potential arriving at the axon terminal brings about the release of acetylcholine, which leads to depolarization of the motor end plate. • Depolarization of the motor end plate triggers an action potential that propagates along the sarcolemma and down the T Tubules. • This action potential causes the release of calcium ions from the terminal cisternae into the cytosol, triggering contraction of the muscle cell. 21. (P 14.) Place the following events in their proper sequence: _____ a. Acetyl choline is released into the synaptic cleft. _____ b. Action potential propagates along the sarcolemma and down the T Tubules. _____ c. Synaptic vesicles fuse to membrane of axon terminal. _____ d. Motor end plate becomes depolarized. _____ e. Action potential is initiated on the sarcolemma. _____ f. Action potential arrives at the axon terminal. _____ g. Calcium ions are released from the terminal cisternae. _____ h. Acetylcholine binds to receptor sites on the motor end plate. _____ i. The muscle cell contracts. _____ j. Calcium ions enter the axon terminal. DO THE QUIZ!! Quiz question #6. Watch this animation carefully. Many poisons and drugs work like molecule X. Describe how molecule X prevents a muscle contraction. What drug or poison has an action like molecule X? Quiz question #7. Watch this animation carefully. Many poisons and drugs work like molecule Y. Describe how molecule Y causes continuous muscle contraction. What drug or poison has an action like molecule Y? Quiz question #8. Watch this animation carefully. Many poisons and drugs work like molecule Z. Describe how molecule Z causes continuous muscle contraction. What drug or poison has an action like molecule Z? 1. What insulates each muscle cell? 2. Synaptic vesicles in the axon terminal of a motor neuron contain what neurotransmitter? 3. An action potential in the axon terminal of a motor neuron opens what type of ion channels? 4. By what means of membrane transport does the neurotransmitter leave the axon terminal? 5. Binding of neurotransmitter to the receptors on the motor endplate open what type of ion channels? 6. Opening of these channels leads to ___________________________ of the motor endplate. 7. How is the neurotransmitter removed from the synaptic cleft? 8. As a result of question 6, an action potential is propagated along the _______________________ of the muscle cell and down the _____________________________ into the cell. 9. The result of this action potential releases what ion from the terminal cisternae? ________














![Neuron [or Nerve Cell]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000229750_1-5b124d2a0cf6014a7e82bd7195acd798-150x150.png)