* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download stroke - UCSD Cognitive Science
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurobiological effects of physical exercise wikipedia , lookup
Perivascular space wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive interview wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive flexibility wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
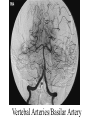
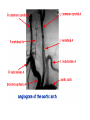
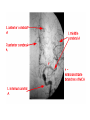
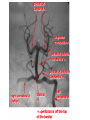
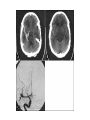
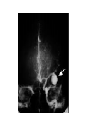
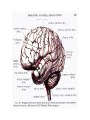
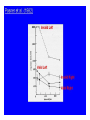
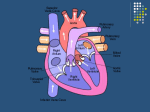
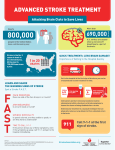
STROKE Vascular System • Reminder: All brain function is dependent on oxygen. • There are two main arterial supplies to the brain: – Carotid Arteries – Basilar Artery (comes off of vertebral arteries) Identify the following arteries in the cerebral angiogram in the image above: Vertebral Artery - Basilar Artery Vertebal Arteries/Basilar Artery Right Internal Carotid Artery Stroke • Reduction in or disruption of Blood Flow to the brain • Two major categories: – Ischemic (blockage of artery) – Hemorrhagic (damage or tear in artery) A side category: • TIA or Transient Ischemic Attack. • Typically involves small emboli in an artery that resolves rapidly. • Thus, the physical or cognitive effects typically resolve within an hour to 24 hours. • There is rarely persistent damage following a TIA • TIAs are often a signal of an impending stroke. Mechanisms of Brain Damage • Excitotoxic Cell Death – Via excitatory amino acid release – Excess calcium flow – Free-radical release, etc. PARP (enzyme involved in cell repair via ATP turnover) – excess ATP turnover – cell death. Pnumbra (excess damage or halo surrounding vascular damage). “Stroke” • Often viewed as motor and speech phemomenon – due to the prevalence of middle cerebral artery stroke. • Stroke can occur in any location and symptoms will map onto the brain region that has undergone O2 deprivation. Medical Issue • Physical Deficits rather than cognitive deficits attract the most attention after stroke. • Physical rehabilitation is readily prescribed. • 50-75% of stroke patients have persistent cognitive impairments after stroke. Clinical Issues to Resolve • Obviously, the cognitive problems associated with stroke are going to vary in relation to the region. • Damage to certain cortical targets may generate notable cognitive signs: amnesia, alexia, agraphia, apraxia, agnosia, etc. • These signs often exist alongside “non-cognitive” signs such as emotional instability or loss of initiative. • There is often depression following stroke. It is difficult to disentangle the axis of depression from that of cognitive dysfunction. Vascular Dementia or Multi-Infarct Dementia • Accumulated Cortical Infarcts Distributed across cortical networks • Strategic Subcortical Infarcts – Generally disconnect the prefrontal cortex from the thalamus or basal ganglia (thalamus + BG and/or genu of internal capsule, etc. • Cortical disconnection syndrome – Often white matter lesions (associated with hypofunction of cortical regions as well). The Classic Case of the Rt. MCA CONCLUSION • Vascular incidents must be carefully followed, to prevent recurrence. • Multiple vascular events may result in a dementia complex. • Both physical and occupational/cognitive therapy are important in promoting remapping following stroke.