* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 6. Cardiovascular Diseases - Blyth-Biology11
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
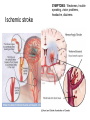
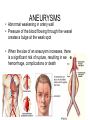
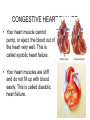
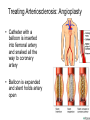
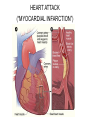
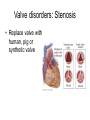
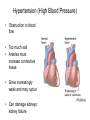
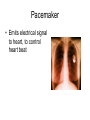
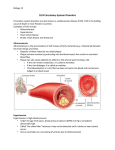
CIRCULATORY DISORDERS Lesson 6 HEART HEALTH 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Cholesterol Smoking Diabetes Hypertension Exercise Weight Genetics Cardiovascular disease deaths • Every 7 minutes in Canada, someone dies from heart disease or stroke. • Heart disease and stroke are two of the three leading causes of death in Canada. HEART MURMURS • A heart murmur is an extra or unusual sound heard during a heartbeat • No symptoms • Usually harmless ANEMIA • Lower than normal amount of oxygen reaching tissues due to: – Low number of red blood cells – Less hemoglobin in red blood cells than normal – Sickle cell anemia (abnormally shaped red blood cells) LEUKEMIA • Cancer of the blood or bone marrow, where white blood cells are overproduced • These extra white blood cells are immature or dysfunctional, and create a harmful RBC / WBC imbalance ANGINA Angina treatment • Nitroglycerin dilates coronary arteries, allowing blood to reach cardiac muscle tissue Ischemic stroke SYMPTOMS: Weakness, trouble speaking, vision problems, headache, dizziness ANEURYSMS • Abnormal weakening in artery wall • Pressure of the blood flowing through the vessel creates a bulge at the weak spot • When the size of an aneurysm increases, there is a significant risk of rupture, resulting in severe hemorrhage, complications or death CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE • Your heart muscle cannot pump, or eject, the blood out of the heart very well. This is called systolic heart failure. • Your heart muscles are stiff and do not fill up with blood easily. This is called diastolic heart failure. CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE • As the heart's pumping action is lost, blood may back up in other areas of the body, causing fluid to build up in the lungs, the liver, the gastrointestinal tract, and the arms and legs. • As a result, there is a lack of oxygen and nutrition to organs, which damages them and reduces their ability to work properly. Arteriosclerosis • General condition where walls of arteries thicken and lose their elasticity • Most common form of arteriosclerosis is atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up on the inside of the artery walls • Can occur in any artery and particularly dangerous in arteries that supply the brain, heart, legs and kidneys • May lead to – – – – Angina Blood clots Heart attack stroke Treating Arteriosclerosis: Angioplasty • Catheter with a balloon is inserted into femoral artery and snaked all the way to coronary artery • Balloon is expanded and stent holds artery open Angioplasty • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fL3Aak_PI-I HEART ATTACK (“MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION”) Treating Arteriosclerosis: Coronary Bypass • Section of healthy artery or vein from another part of the body (usually leg) is removed and put in place of blocked coronary artery • Double, triple or quadruple Symptoms • Uncomfortable pressure in chest lasting more than a few minutes • Pain spreading from chest to the shoulders, neck or arms, upper abdomen, neck, jaw, or inside the arms or shoulders • Lightheadedness, fainting, sweating, nausea or shortness of breath • Anxiety, nervousness and/or cold, sweaty skin. • Paleness • Increased or irregular heart rate • Feeling of impending doom. CPR: CARDIO-PULMONARY RESUSCITATION • If you find someone who seems to be NOT breathing with NO pulse... – Try to wake them up! – Open airway: head-tilt, chin-lift – Check for breathing again by watching for chest rising/lowering • Still not breathing? – Two mouth-to-mouth breaths • Still not breathing? – CPR: 30 two-handed, rapid, deep-chested, firm compressions – Follow with head-tilt, chin-lift + two mouth-to-mouth breaths – And repeat... Drugs and the Heart • Digitalis – found in foxglove – treat heart failure • Beta blockers – block sites on heart for epinephrine – slow down heart rate (Angina: reduce O2 demand) Valve disorders: Stenosis • Replace valve with human, pig or synthetic valve Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) • Obstruction to blood flow • Too much salt • Arteries must increase connective tissue • Grow increasingly weak and may rupture • Can damage kidneys: kidney failure Arrhythmia • Irregular heart beat • Blocked coronary artery – Buildup of toxins – Cause part off heart to beat out of rhythm = ventricular fibrillation • Congenital heart defect – Weak valves – Backflow affects rhythm Pacemaker • Emits electrical signal to heart, to control heart beat Learning Check • Pg 498, Q 19-24 Congenital Heart Defects • Since birth • Holes in septum • Valve disorders Diagnosing Circulatory System Disorders • Angiography • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kY5gKdFWT3k • Echocardiogram • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0eKdhHF-JLg • Cardiac stress test • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x_Z0GF6AuTw Organ Transplants • Xenotransplants • Artificial heart