* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Passive and Active Transport
Survey
Document related concepts
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
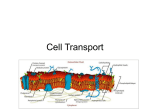
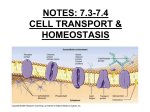
Cell Membrane Phospholipid bilayer – two layers of phospholipids back to back Phosphate Heads – polar – water soluble - hydrophilic Lipid Tails – non-polar – water insoluble – hydrophobic Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Cholesterol stabilizes the membrane by preventing the lipid tails from sticking together Proteins help regulate what enters and exits the cell Carbs stick out from the membrane to identify chemical signals What is Cell Transport? Discovering how molecules travel across the cell membrane. Maintains homeostasis for the cell There are 2 types of transport Passive Transport Passive Transport – moving particles across the cell membrane from high to low concentration using no energy There are 3 examples Passive Transport Facilitated Diffusion – uses channel or carrier proteins to move molecules from a high to low concentration Channel proteins allow easier travel for larger molecules Carrier proteins change shape to help molecules to travel through Diffusion – moving any type of molecule across the cell membrane from a high to low concentration Facilitated Diffusion Diffusion Osmosis Osmosis – diffusion of water across a cell membrane Water travels from a high to low concentration Concentration Gradient – unequal distribution of particles that controls osmosis 3 different solutions But First… Solute – a substance that is dissolved in another substance Ex. Salt, Sugar Solvent – a substance that dissolves other substances Ex. Water Osmosis Isotonic Solution – the concentration of the solute inside the cell is the same as the concentration of the solute outside of the cell Water moves in and out of the cell at the same rate Isotonic Solution Osmosis Hypotonic Solution – The concentration of solute outside the cell is smaller than inside the cell There is more water outside the cell than inside Water moves into the cell The Cell Swells Hypotonic Solution Hypertonic Solution Hypertonic Solution – The concentration of solute outside the cell is greater than inside the cell There is more water inside the cell than outside Water moves out of the cell The Cell Shrinks Hypertonic Solution Active Transport Active Transport – moving particles across the cell membrane from low to high concentration using energy Uses carrier proteins Uses 2 Processes Active Transport Endocytosis – the cell membrane encloses and forms around large particles in order to let it pass through Exocytosis – the expulsion of materials, waste, and hormones from the cell Transport Protein Protein embedded in the cell membrane responsible for picking up or passing molecules through the cell membrane. This requires energy. Endocytosis Exocytosis Why Is Active Transport Important? Rid the cell of toxins Movement to avoid danger or to find food, water, and or mates Synthesizing needed molecules