* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Why is the cell membrane so important?
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
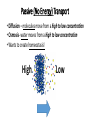
Why is the cell membrane so important? Cell Membrane Basics 1. Also known as the plasma membrane 2. Semi-permeable-only some material can get in or out 3. Has a phospholipid bilayer inside cell outside cell Semi-Permeable Membrane • Controls what gets in or out • Needs to allow some materials — but not all — to pass through the membrane inside cell waste outside cell lipid salt sugar aa H 2O Semi-Permeable Membrane What gets in easily? 1. Lipids 2. Water Why? 1. Channels are made out protein; “likes” both water and lipids Semi-Permeable Membrane Movement • Movement Types: • Passive Transport- No energy required • Active Transport- Energy required (ATP) Passive (No Energy) Transport • Diffusion – molecules move from a high to low concentration • Osmosis- water moves from a high to low concentration • Wants to create homeostasis! High Low Osmosis Water balance is important! 1. Hydrated 2. Dehydrated 3. “Drown” Hypotonic Solution: Higher concentration of fresh water outside of the cell. Cell swells and bursts. Hypotonic Solution: Equal amount of fresh water inside and outside of cell. Hypertonic Solution: Lower concentration of fresh water outside of the cell. Cell shrinks. Two Types of Diffusion • Simple Diffusion: Osmosis and Diffusion • Facilitated Diffusion: • Uses protein pump due to size of molecules Active Transport • Molecules move from low to high • Requires energy (ATP) VS Active Transport • Endocytosis: Engulfs/Brings in molecules • Exocytosis: Allows molecules and waste to exit a cell