* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Transport - Northwest ISD Moodle
Survey
Document related concepts
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Implicit solvation wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
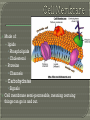
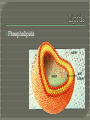
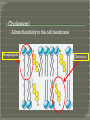
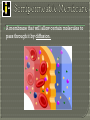
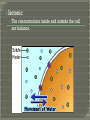
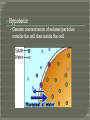
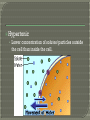
What goes in? What goes out? Membrane • A thin layer-like structure that separates two fluids. • Allows some particles/chemicals to pass through, but not others. Made of: • lipids Phospholipids Cholesterol • Proteins Channels • Carbohydrates Signals Cell membrane semi-permeable, meaning certaing things can go in and out. Phospholipids Cholesterol • Allows flexibility to the cell membrane Phospholipids Cholesterol Protein Channels • Allow particles to go in and out of the cell • REQUIRE ENERGY (most of the time) A membrane that will allow certain molecules to pass through it by diffusion. Passive Transport • Does NOT require energy to move material in and out the cell Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion (Requires Protein Channel) Active Transport (Requires Protein Channel) • Requires energy (ATP) to move materials in and out the cell Antiport Symporter Uniporter Particles (which are constantly moving) move from areas of high concentration to low concentration. Eventually Diffusion the particles spread evenly. does NOT require energy. Diffusion of WATER through a selectively permeable membrane. When the particles are too big to fit through the membrane, WATER moves from high to low. Solution • A mixture of 1 or more solutes in one solvent. Solvent • Substance in which a solute dissolve Solute • Substance that dissolves to form a solution Solute Solvent Isotonic • The concentrations inside and outside the cell are balance. Hypotonic • Greater concentration of solutes/particles outside the cell than inside the cell Hypertonic • Lower concentration of solutes/particles outside the cell than inside the cell. Antiport • Protein channel two ions or solutes are pumped in opposite direction across a membrane. Symport • Protein channel that allows two or more ions/molecules to move across the membrane in the same direction