* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Changes in DNA can produce variation
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
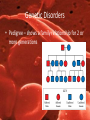
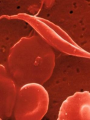
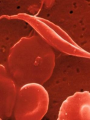
Changes in DNA can produce variation Section 5.2 DNA sequence can change • Differences in DNA are what make one organism different from another • The number of differences between two species is large Human 3 billion Base pairs Yeast cell 12 Million Base Pairs DNA sequence can change • The number of differences between 2 individuals of the same species is small • (<0.1% variation) DNA sequence can change • There is a large number of DNA bases in any organism that need to be copied • Errors can occur when DNA is copied or affected by environment – UV radiation – X-rays – Toxins DNA sequence can change • Mutation – any change in DNA • Cells have ways of fixing mistakes in DNA • However some mistakes are not fixed Possible outcomes when error occurs in genes No effect – Some amino acids have more than one code and may not change resulting protein – May have enough protein being produced Possible outcomes when error occurs in genes • Mutation is minor – May only cause a change in appearance Possible outcomes when error occurs in genes Mutation is great – Could be good (Resistant to disease) – Could be bad (genetic disorder or disease) • Only 5% of human DNA is in genes • If mutation occurs in a non-coding region, then chances are that the mutation is neutral Genetic Disorders • Disease or condition caused by mutations that affect normal functions of the cell – Can be inherited (Tay-Sachs) – Can occur during a person’s life (Cancer) Genetic Disorders • A person can carry a tendency for a disease (diabetes) • Sometimes a person’s behavior can prevent the disease (smoking) Genetic Disorders • Mutations can have more than one effect – Sickle cell anemia • Recessive disorder • Prevents blood from carrying oxygen • Prevents malaria Genetic Disorders • Pedigree – shows a family relationship for 2 or more generations Cancer • • • • A group of disorders Characterized by uncontrolled division of cells Cells can spread to other tissues Causes – Inherited – Carcinogens – Radiation – Series of mutations