* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2: Brain Development
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
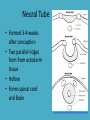
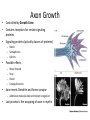
Chapter 2: Brain Development TJHSST Neuroscience Society Prepared by Usnish Majumdar Development • First neurons must be created (differentiated cells) • Neurons must then migrate • Axon-dendrite migration and connection occurs 3 Layers of Embryo • Ectoderm (“ecto” latin = outside) – Skin – Neural Tissue • Mesoderm (“middle” latin = middle) • Endoderm (“endo” latin = within) http://faculty.clintoncc.suny.edu/faculty/michael.gregory/files/Bio%20102/Bio%20102%20lectures/Animal%20Diversity/Protosto mes/Lophotrochozoans/Image7.gif Neural Tube • Formed 3-4 weeks after conception • Two parallel ridges form from ectoderm tissue • Hollow • Forms spinal cord and Brain http://scienceblogs.com/retrospectacle/2007/06/neurological_defect_spotlight.php Cell Differentiation • Most embryonic cells are pluripotent stem cells • A variety of chemicals signal cells to turn into specialized cells • Ectodermal cells are inhibited by molecules, signalling a development into neural cells and not skin cells • After neural cell determination: – – – – Sonic hedgehog – protein secreted from mesoderm Higher concentration = glial cell Lower concentration = motor neuron Even lower concentration = interneuron More Cell Differentiation (Yes, this is important) • Signals help determine the specific neurotransmitters that can be used by a neuron • If neurons are cultured by themselves = norepinephrine • Cultured with cardiac tissue = acetylcholine • Based on different genes turning off and on Neuronal Migration in The Brain •Neurons produced in center of tube, migrate outward •Ventricular zone -> Marginal zone •Migration prominent in cortex •Mechanisms •Neurons migrate along fibers to destination •inhibitory interneurons migrate tangentially •External forces that can disrupt proper neuronal migration: •Alcohol, Cocaine, Radiation, etc. Connections • Axons travel long distances until they find dendrites • In the case of a motor neuron, axon may travel from spinal cord to foot Axon Growth • Controlled by Growth Cone • Contains receptors for certain signaling proteins • Signaling proteins (actually classes of proteins) – Netrin – Semaphorins – Ephrins • Possible effects – – – – Move forward Stop Recoil Change Direction • Axon meets Dendrite and forms synapse – Additional molecules help with target recognition • Last process is the wrapping of axon in myelin Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Paring Back • Neural network is ‘pruned’ to create a more efficient and accurate system (too many connections at first) • Apoptosis: programmed cell-death – AP Biology: regulated by several proteins • Neuron doesn’t receive enough trophic factor to deter these proteins, it dies • Each trophic factor supports a specific group of neurons – Ex: nerve growth factor = sensory neuron survival Critical Periods • Important period when nervous system must obtain certain critical experiences. • “use it or lose it” • Enriched environments bolster brain development Development Continues • Even in your late teens, your brain is still maturing. • Frontal lobe is last to become connected with myelinated axons – Judgement, insight, and impulse control – …college students … Quiz: 5 minutes, 15 Questions