* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download trp
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Control Mechanisms
{
Miss Richardson
SBI4U
There are four levels of control of gene
expression:
1.
-Regulates which genes are
Transcriptional transcribed
-Controls rate of transcription
2. Post-Modification of mRNA
transcriptional -Introns removed and exons
spliced together
Control of Gene
Expression
There are four levels of control of gene
expression:
3. Translational -Controls rate of translation
-Controls rate of mRNA activation
and destruction
4. Posttranslational
-Controls rate at which a protein
becomes active and the time it
remains functional
Control of Gene
Expression
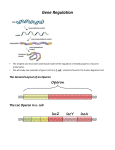
E. coli uses β-galactosidase to break down
lactose in order to grow.
The 3 genes for β-galactosidase are part
of the lac operon.
The lac Operon
When lactose is absent:
LacI repressor protein binds to the
operator and partially blocks the
promoter.
Prevents transcription of the lac
operon genes
The lac Operon
With sufficient lactose:
Binds to the LacI repressor protein.
LacI changes its shape, allowing
transcription of the lac operon genes
The lac Operon
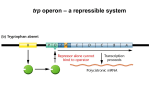
E. coli uses tryptophan for the production
of protein.
The trp operon consists of 5 genes that
code for 3 enzymes needed to synthesize
tryptophan.
The trp Operon
When tryptophan is absent:
The shape of the trp repressor
protein changes.
No longer binds to the trp operator.
RNA polymerase transcribes trp
operon genes.
The trp Operon
With sufficient tryptophan:
Binds to the trp repressor protein,
causing a change in shape.
trp repressor-tryptophan complex
binds to the operator.
Prevents transcription of the trp
operon genes.
The trp Operon
lac Operon
Transcription induced when high levels
of lactose present.
Effector = level of lactose
trp Operon
Transcription repressed when high levels
of tryptophan present.
Effector = level of tryptophan
Summary