* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 18: Control of Gene Expression in Bacteria
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Quorum sensing wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
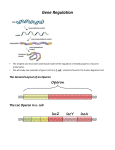
Chapter 18: Control of Gene Expression in Bacteria Text Vocabulary: Gene Expression Transcriptional Control Translational Control Post-translational Control Constitutively Inducer Mutagens Replica Plating Medium Constitutive Mutants Negative Control Repressor Positive Control Activator Operon Lac operon Operator Allosteric Regulation Ara operon AraC Global gene regulation Regulon Lecture 30 “Negative Control of Gene Expression in Bacteria” PPT Review 1.) What category of macromolecules would lactose fall under? Based on the double ring structure of lactose, how would it further be classified under this macromolecule family? 2.) What is the function of the proteins Galactoside permease and β-Galactosidase? 3.) What is an operon? 4.) What are the genes encoded by the lac operon promoter? Is lacI transcribed from the same lac operon promoter? Which genes express β-Galactosidase and Galactoside permease? 5.) What is an Operator in terms of prokaryotic operons? Based on its function, what would the operator be classified as? 6.) What is the function of the protein expressed from LacI? When it interacts, what part does it interact with on its target and what structure of the protein allows this? 7.) The protein coded by the LacI gene can be altered in a way that changes its function. What is the name of this change and what induces the change to this protein? 8.) Is the lac operon an example of positive or negative control? Based on the mechanism, explain why. How can this type of control then be suppressed? (Explain the difference between lactose being present and absent) 9.) How does glucose affect the transcription of the lac operon? Why? What is it interacting with to cause the effect? Lecture 31 “Positive Control of Gene Expression in Bacteria” PPT Review 1.) What are all the components of the DNA comprising the ara operon? 2.) How does the araC act as a regulatory protein in the presence and absence of arabinose? 3.) Slide 9 question: “The bacteria glow in response to a molecule that regulates expression of genes involved in light-producing chemical reactions. The regulator controls production of the genes’ mRNA. Therefore, the light-producing genes are under ____ “ 4.) Explain the LuxR regulation occurring on Slide 11. 5.) Slide 12 question: LuxR is allosterically regulated by the signaling inducer molecule secreted by V. fischeri. What does it mean that LuxR is allosterically regulated? 6.) What is a regulon? What is the benefit of regulon for bacterial survival? How are they different from operons? 7.) How does Vibrio cholera respond to quorum sensing in the human gut? 8.) Slide 16 question: “Why might quorum sensing be beneficial to pathogenic bacteria?”