* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transport in plants
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
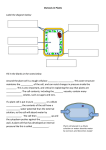
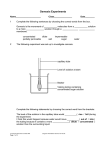
Transport in plants Grade 8 biology Diffusion A type of passive transport(not requiring energy) involving the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Diffusion is spontaneous and automatic. Osmosis passage of water from a region of high water concentration, through a semipermeable membrane, to a region of low water concentration. Endosmosis inward osmosis inward passage of liquid through a membrane of a cell or cavity Exosmosis outward osmosis outward passage of liquid through a membrane of a cell or cavity Plasmolysis Hypertonic hypotonic and isotonic solutions Videos on Elodea in hypertonic solution Elodea in hypotonic solution Demonstration Turgor pressure( video) also called turgidity, is the main pressure of the cell contents against the cell wall in plant cells. Turgor is a force exerted outward on a plant cell wall by the water contained in the cell. This force gives the plant rigidity, and may help to keep it erect. Turgor can result in the bursting of a cell. Exercise Write a letter from the cell membrane to cell wall of a plant cell, explaining how their closeness or interactions depend on the availability of water in their respective surroundings. Make sure you use all the terms you have learnt till now !! Wall pressure It is the pressure exerted by the cell wall on the contents of the cell, including the cell membrane. Turgid and flaccid cells Plant cells need to be turgid (i.e rigid) to support plant tissues. Plant cells become turgid when water moves into the cell by osmosis, and the central vacuole swells and pushes against the cell wall. When plant cells are placed in concentrated sugar solutions they lose water by osmosis and they become "flaccid"; this is the exact opposite of "turgid" Turgid plant cells contain more water than flaccid cells and exert a greater osmotic pressure on its cell walls.