* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA-RNA Review
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
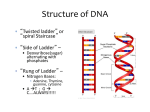
RNA, DNA, & Proteins Chapter 9 & 10.1 Review Main enzyme involved in linking nucleotides into DNA molecules during replication DNA polymerase Another name for protein synthesis translation Sugar used to make DNA dexoyribose Process of making a DNA copy replication Nitrogen base with 1 ring such as cytosine and thymine pyrimidine Organism whose cells have a nucleus eukaryote Process in which the genetic code of DNA is copied into a strand of RNA transcription Three sequential nucleotides in an mRNA molecule that code for a specific amino acid codon Organism without a nucleus prokaryote Nitrogen base with 2 rings like adenine and guanine Purine Subunit composed of a sugar, nitrogen base, and a phosphate group used to make DNA and RNA nucleotide Principle that hydrogen bonds can only form between certain nitrogen bases Base pairing Group of three nucleotide bases on a t-RNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon anticodon Process of making proteins from an RNA message Translation (protein synthesis) What is CHARGAFF’S RULE? A = T G = C Image from: http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evosite/evo101/images/dna_bases.gif Type of RNA that carries DNA code from the nucleus out to the cytoplasm Messenger RNA Segment of DNA that codes for a protein gene Region of DNA where RNA polymerase binds to start transcription promoter Bonds between nitrogen bases that hold the 2 DNA strands together Hydrogen bonds Type of RNA that matches its anticodon and attaches the correct amino acid to the growing protein chain during protein synthesis Transfer RNA Structures found in the cytoplasm made of rRNA and proteins where protein synthesis happens Ribosomes Type of RNA that combines with proteins to make ribosomes Ribosomal RNA Sugar found in RNA molecules ribose Enzyme that binds to DNA, separates the strands, and assembles nucleotide subunits into an RNA molecule RNA polymerase Macromolecule made by joining nucleotide subunits together Nucleic acid (DNA & RNA) Another name for a protein chain polypeptide Macromolecule made by joining amino acid subunits together protein Name the woman scientist whose X-ray images of DNA helped James Watson and Francis Crick figure out the structure of DNA ROSALYN FRANKLIN http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rosalind_Franklin http://www.time.com/time/time100/scientist/profile/watsoncrick.html Tell 2 ways DNA is different from RNA DNA Double stranded Deoxyribose sugar A,T,C,G No Uracil RNA Single stranded Ribose sugar A,U,C,G No thymine Contains genetic code Stays in nucleus Carries code from nucleus to cytoplasm Helps with protein synthesis Making a DNA copy = _____________ replication Using DNA code to transcription make an RNA = ___________________ Using an RNA message translation to make a protein = _______________ Name the two scientists received the Nobel prize for figuring out the structure of DNA JAMES WATSON & FRANCIS CRICK http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rosalind_Franklin http://www.time.com/time/time100/scientist/profile/watsoncrick.html DNA → DNA = _____________ replication DNA → RNA = ___________________ transcription translation RNA → protein = _______________ Name this subunit used to build nucleic acids like DNA & RNA Image by: Riedell NUCLEOTIDE If this was going to make RNA what sugar would be used? ribose Which nitrogen base THYMINE could NOT be used? Name this subunit used to build nucleic acids like DNA & RNA Image by: Riedell NUCLEOTIDE If this was going to make DNA what sugar would be used? deoxyribose Which nitrogen base URACIL could NOT be used? Tell what nitrogen base these letters stand for _____________= ADENINE A _____________ GUANINE = G _____________ CYTOSINE = C ______________ THYMINE = T URACIL = U ______________ Which molecules make up the backbone (sides of ladder) in a DNA molecule? Sugar and phosphates Image from: http://www.tokyo-med.ac.jp/genet/picts/dna.jpg Nitrogen bases with 2 rings are called ______________ A G Purines © Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved Nitrogen bases with 1 ring are called ______________ C Pyrimidines T © Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved Hydrogen _____________ bonds between nitrogen bases hold the two strands together. Image from: http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evosite/evo101/images/dna_bases.gif New strand Original strand DNA polymerase Growth DNA polymerase Growth Replication fork Replication fork New strand Original strand Nitrogenous bases The sites where strand separation and replication forks replication occur are called _____________ Name the 3 kinds of RNA RIBOSOMAL _________________RNA Combines with proteins to form ribosomes TRANSFER _________________RNA Matches m-RNA codon to add correct amino acids during protein synthesis _________________RNA MESSENGER carries code from DNA to ribosomes rRNA and t-RNA images from © Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved mRNA image from http://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/tmp/labeling/1140654_dyn.gif Use the mRNA codon wheel to determine the amino acid being coded for: proline C C A =___________ arginine C G U = __________ phenylalanine U U C = __________ alanine G C A = __________ STOP U A G = __________ Name the 3 kinds of RNA RIBOSOMAL _________________RNA TRANSFER _________________RNA MESSENGER _________________RNA rRNA and t-RNA images from © Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved mRNA image from http://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/tmp/labeling/1140654_dyn.gif NUCLEUS A= _________ m-RNA B= _________ amino acid ribosome C= _________ t-RNA D= ___________ codon F= _____________ acid G = Amino __________________ Images modified from © Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved