* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells 10th class
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
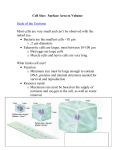
CELLS THE BASI C UNI T OF LI FE -THE SMALLEST UNI T THAT CAN CARRY OUT ALL OF THE ACTI VI TI ES OF LIFE THE CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of living things 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells I. ALL LIVING THINGS ARE MADE FROM CELLS 1) Unicellular: Single – celled organisms 2) Multicellular: organisms made of many cells WHY ARE CELLS SMALL? Cell Size Activity II. LIMITATIONS ON CELL SIZE • 3 Limitations on cell size: 1. 2. 3. A cell’s parts cannot be too far from the membrane Cell volume increases faster than its surface area The rate of diffusion is slow, so cells can only move materials at a slow rate III. TYPES OF CELLS 1. Prokaryotic Simple cells that lack an organized nucleus and membrane bound organelles (organelles with membranes) All Prokaryotic organisms are single-celled organisms Bacteria Oldest Forms of Life PROKARYOTIC CELL Flagella Nucleoid (DNA) Cell Membrane Ribosomes Pili Capsule Cell Wall III. TYPES OF CELLS 2. Eukaryotic Cells Larger cells that contain a membrane bound nucleus and membrane bound organelles Can be…. Single-Celled (unicellular) or multicellular (all plants and animals) ANIMAL CELL PLANT CELL PLANT CELL Chloroplast Mitochondria Smooth ER Nucleus Cell Wall Nucleolus Cell Membrane Rough ER Cytoplasm Golgi apparatus Vacuole Ribosome ANIMAL CELL COMPARE AND CONTRAST A PROKARYOTIC VS. EUKARYOTIC CELL Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell COMPARE AND CONTRAST A PROKARYOTIC VS. EUKARYOTIC CELL No Nucleus Single-Celled Bacteria No Membrane Bound Organelles Generally smaller Simple Cells Contain genetic Material (DNA or RNA) Cell Membrane Nucleus Single Celled or MultiCellular Organisms Membrane Bound Organelles Larger and more complex Ribosomes Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell IV. STRUCTURE AND SUPPORT o Cell Membrane- protects and contains the contents of the cell; important barrier allowing some substances to enter and leave but not others (double phosopholipid bilayer) o Cytoplasm- the mostly fluid internal part of the cellcontains and bathes the organelles (a colloid like gelatin) IV. TYPICAL CELL STRUCTURES FOUND IN CELLS o Cytosol – the fluid part of the cytoplasm (watery) o Cytoskeleton – Supports and gives structure and strength to the cell, made of microtubules STRUCTURE AND SUPPORT CELL WALL • The cell wall is made of cellulose. It is found in plants in addition to the cell membrane. The cell wall provides protection and structural support. • Some bacteria and fungi cells also have cell walls that are not made out of cellulose. RIBOSOMES (FOUND IN ALL CELLS) • Ribosomes are small round organelles that make proteins based on the instructions provided by the DNA. • Ribosomes are located in the cytosol or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes attached to the ER IV. TYPICAL EUKARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURES o Organelles: “little organs”- structures in the cell that carry out various functions The number and kind of organelles in a cell will often determine what kind of cell it is Without organelles to perform different functions, multicellular life would not be possible Organelles provide compartmentalization that provides suitable environments for chemical reactions to take place. Membranous organelles provide greater surface areas for reactions to take place ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM NUCLEUS Nucleus – contains DNA, controls cell activity macronucleus: reproduction micronucleus: control cell functions NUCLEOLUS • Nucleolus • Located inside the nucleus • The nucleolus manufactures ribosomes NUCLEAR ENVELOPE • Nuclear Envelope is the membrane that surrounds the nucleus • The Nuclear Envelope controls what molecules are able to enter or leave the nucleus ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM • The ER could be compared to the cell’s “highways” • Rough ER: This is the location where proteins are modified and transported through the cell • In the Smooth ER, lipids are produced and stored. Chemical reactions required by the cell take place here. ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM GOLGI APPARATUS • The Golgi apparatus can be compared to a factory and a post office • The Golgi apparatus changes, packages, and distrubutes products to other areas of the cells • For example the Golgi apparatus is responsible for packaging proteins and other macromolecules to be “shipped” outside of the cell MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES MITOCHONDRIA • The Powerhouse of the Cell • This is the location of Cellular Respiration • In other words this is where food is converted into energy Cell Respiration: C6H12O6 + 6O2 Sugar + Oxygen 6CO2 + 6H2O Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP (Energy) MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES CHLOROPLASTS • Chloroplasts are found in plants • Chloroplasts are a class of plastids that contain chlorophyll, a pigment used in photosynthesis. This is the location of photosynthesis where glucose is produced and starch may be stored. • Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O Carbon Dioxide + Water C6H12O6 + 6O2 Sugar + Oxygen ORGANELLES LYSOSOMES • Lysosomes are found mainly in animal cells • Lysosomes contain enzymes for digesting macromolecules, old organelles, bacteria, viruses, etc. ORGANELLES PEROXISOMES • Peroxisomes are found in animal cells. • Peroxisomes contain enzymes that create hydrogen peroxide to break down fats, and to perform other metabolic processes ORGANELLES VACUOLES • Vacuoles are very large when found in a plant cell. • Vacuoles are large membrane-bound vessels for digestion and storage. Vacuole PLANT STRUCTURES/ ORGANELLES LEUCOPLASTS • Leocoplasts store starch. PLANT STRUCTURES/ ORGANELLES CHROMOPLASTS • Chromoplasts are another type of plastid. • Chromoplasts store pigments. They are the source of color for flowers and some vegetables. The colors serve to attract insects, birds, and animals. COMPARE AND CONTRAST PLANT AND ANIMAL CELL