* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology-Soto
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
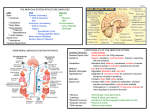
Chapter 33 Nervous System 1 Sect 33.2 – Organization of the Nervous System 2 33.2 Organization of the NS Objectives •Describe the major divisions of the nervous system. •Compare and contrast the somatic nervous system with the autonomic nervous system. 3 33.2 Organization of the NS Main Idea •The central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system are the two major divisions of the nervous system. 4 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •Nervous system consists of two major divisions ◦ the central nervous system (CNS) ◦ the peripheral nervous system (PNS) •CNS ◦ has two major structures brain spinal cord 5 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •CNS ◦ composed most of interneurons ◦ function to coordinate all of the body’s activities ◦ the CNS relays messages processes information analyzes responses 6 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •Typical pathway ◦ sensory neuron pass info to the spinal cord interneurons in the cord might □ respond via a reflex arc □ relay the info to the brain ◦ in the brain info processed in at least 2 ways □ brain tissue sends message to motor neurons ~ via the cord ~ body reacts accordingly □ info may be stored for later use 7 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •Brain ◦ weighs an average of 1.4 kg (3 lbs) ◦ composed of about 100 x 109 neurons ◦ has two major functions overseeing the daily operations of the body interpreting all of the info it receives ◦ composed of 3 major parts cerebrum brain stem cerebellum 8 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •Brain Cerebellum Cerebrum Brain Stem 9 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •Cerebrum ◦ largest and most prominent area of the human brain ◦ functions of the brain include thought processes (learning) memory language speech voluntary body movements sensory perception 10 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •Cerebrum ◦ deep groove running front to back divides the cerebrum into L & R hemispheres ◦ hemispheres connected by a band of tissue □ called the corpus callosum Corpus Callosum 11 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •Cerebral hemispheres ◦ each cerebral hemisphere deals with the opposite side of the body the left hemisphere □ controls the right side of the body the right hemisphere □ controls the left side of the body 12 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •The Cerebellum ◦ second largest region of the brain ◦ located at the back of the brain ◦ it controls balance posture coordination ◦ it controls skeletal muscle movements so that they are □ coordinated □ smooth 13 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •The Cerebellum Cerebellum 14 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •The Brain Stem ◦ connects the brain and spinal cord ◦ it has two regions: the medulla oblongata the pons ◦ the medulla oblongata helps control breathing rate heart rate blood pressure ◦ The pons aids in breathing 15 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •The Brain Stem Medulla Oblongata Brain stem Pons 16 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •The Hypothalamus ◦ located atop the brain stem ◦ is essential for homeostasis ◦ it regulates body temperature thirst appetite water balance 17 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •The Hypothalamus Hypothalamus 18 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •Spinal Cord ◦ main communications link between the brain the rest of the body ◦ continuous with the medulla oblongata ◦ some info is processed in the cord example: most reflexes ◦ protected by the vertebrae ◦ gives off 31 pairs of spinal nerves 19 33.2 Organization of the NS Central Nervous System •Spinal Cord 20 33.2 Organization of the NS Peripheral Nervous System •PNS ◦ contains all the neurons that are not part of the CNS this includes □ all the nerves □ their associated cells ◦ nerve = a bundle of axons may contain □ only sensory neurons □ only motor neurons □ a mixture of both 21 33.2 Organization of the NS Peripheral Nervous System •PNS includes ◦ cranial nerves ◦ spinal nerves •Cranial nerves ◦ 12 nerves come off the brain □ go directly to areas they serve ◦ mixture of nerves sensory motor mixed 22 33.2 Organization of the NS Peripheral Nervous System •Spinal nerves ◦ 31 pairs of nerves come off the brain □ pass down the spinal cord □ then to their respective area ◦ mostly mixed nerves 23 33.2 Organization of the NS Peripheral Nervous System •PNS ◦ has two major divisions somatic nervous system (SNS) autonomic nervous system (ANS) •Somatic NS nerves relay info ◦ from external sensory receptors to the CNS ◦ from the central nervous system to skeletal muscles 24 33.2 Organization of the NS Peripheral Nervous System •SNS ◦ includes all voluntary muscle movements reflexes ◦ reflex = a quick, automatic response to a stimulus most go only to the spinal cord □ not to the brain 25 33.2 Organization of the NS Peripheral Nervous System •ANS ◦ regulates involuntary activities ◦ activities under subconscious control ◦ carries impulses from the CNS to the □ heart □ other internal organs ◦ has two branches sympathetic nervous system parasympathetic nervous system 26 33.2 Organization of the NS Peripheral Nervous System •Sympathetic NS ◦ is most active in times of emergency stress ◦ causes increases in certain functions heart rate breathing rate ◦ produces the “fight or flight” response 27 33.2 Organization of the NS Peripheral Nervous System •Parasympathetic NS ◦ is most active in times of relaxation ◦ counterbalances the effects of the SNS restores the body to a resting state •Interaction between ◦ sympathetic NS ◦ parasympathetic NS ◦ helps the body maintain homeostasis 28 33.2 Organization of the NS Question •The part of the brain that is responsible for coordination and balance is the a. cerebellum. b. cerebrum. c. brain stem. d. thalamus. 29 33.2 Organization of the NS Question •Reflex arcs are actions that are a part of the peripheral nervous system's a. sensory division. b. somatic system. c. autonomic system. d. motor division. 30 33.2 Organization of the NS Question •Which of the following is NOT under the control of the autonomic nervous system? a. heartbeat b. digestion c. walking d. sweating 31 33.2 Organization of the NS Q U E S T I O N S ?? 32