* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Wall - NVHSIntroBioPiper1
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
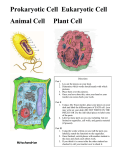
Warm-Up / EOC Prep 1. Structures that give support and shape to plant cells are: A microbodies C nucleus B golgi bodies D cell walls 2. Ribosomes A are the site of protein synthesis B are made by other ribosomes C have their own DNA D none of the above If you have yet to do so, turn in the Final Exam Review packet assigned over break. It is late. If you borrowed a textbook, return it before Friday!! Agenda Warm-Up Notes- Cells and Biomolecules Review worksheets Clean-Up Cool-Down EOC Review DAY 2: ORGANIC MOLECULES AND CELLS Objective 2.02-Cell theory The cell theory was developed with the help of the light microscope The cell theory states that living organisms are composed of cells that arise from pre-existing cells and cells are the basic units of structure and function Cell theory 1. All organisms composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. Two major types of cells: Prokaryotic: no nucleus, no organelles, smaller, came first Ribosomes, cell membrane, cytoplasm Eukaryotic: Nucleus, organelles, bigger, came second Types of Cells Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Organelles • Organelles = little organs that perform specific jobs in the cell • Organelles are found in eukaryotic cells but not prokaryotic cells • Plant and Animal cells are both examples of eukaryotic cells with organelles • Plant and Animal cells contain many of the same organelles, but there are several differences Plant vs. Animal Cells Plant Cells Animal Cells Chloroplasts 2. Cell wall 3. Large vacuole 1. 1. No Chloroplasts 2. No Cell wall 3. Small Vacuole 1. Structures that give support and shape to plant cells are: A microbodies B golgi bodies C nucleus D cell walls Organelles 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Nucleus Ribosomes Mitochondria Chloroplast Vacuole Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi Apparatus Plasma Membrane Cell Wall Nucleus Looks like: Central area where DNA is found Job: controls the cell In a factory: Boss Ribosomes Looks like: Small particles of RNA in the cytoplasm and on the ER Job: make proteins (protein synthesis) In a factory: workers Mitochondria Looks like: a bean Job: powerhouse of the cell-it produces the energy in the form of ATP In a factory: generator (energy source) Mitochondria Mitochondria Chloroplast Looks like: green stacks of membranes the contain chlorophyll Job: perform photosynthesis (convert sunlight into energy) In the factory: greenhouse Vacuole Looks like: sac-like organ. HUGE in plant cells Job: stores water, food, and waste In a factory: storage room Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Looks like: internal membrane system next to the nucleus (rough ER has ribosomes, smooth ER does not) Job: transports materials In a factory: conveyor belt Golgi Apparatus Looks like: stack of membranes Job: Packs, sorts, and ships In a factory: packaging center Plasma Membrane Looks like: layered membrane (called a lipid bilayer) surrounding the cell but inside of the cell wall Job: “the regulator”-controls what comes in and out of the cell, protects, and supports the cell In a factory: security guards Cell Wall Looks like: thick layer outside the plasma membrane Job: structure and support In a factory: Cement wall 1. Ribosomes A are the site of protein synthesis B are made by other ribosomes C have their own DNA D none of the above 2. The mitochondrion of the cell A has only one membrane B has no membrane C is circular D is where cellular respiration occurs 3. The storage of hereditary information in a eukaryotic cell is in the A cytoplasm B nucleus C centrioles D lysosomes Objective 2.01-Organic Molecules • “Organic” = has carbon • “Inorganic” = no carbon • Monomer + Monomer + Monomer = Polymer • Monomer of proteins = amino acids • Monomer of lipids = fatty acids • Monomer of nucleic acids = nucleotides • Monomer of carbohydrates = sugar • Example: starch is made up of glucose Testing for organic molecules Benedicts-test for sugar Iodine-tests for starch-turns blue Brown paper test-tests for lipids-becomes translucent with lipids 1. Nucleotides are to nucleic acids as amino acids are to… A DNA B polypeptides C proteins D carbohydrates Objective 2.04-Enzymes • Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts to speed up chemical reactions • Catalysts speed up reactions by lowering activation energy • Enzymes can be affected by the following factors: 1. Temperature 2. pH • Extreme temperature or changes in pH cause enzymes to denature (become destroyed) 1. enzymes are A catalysts used by living things B catalysts used in all reactions C chemicals used to increase activation energy D fats used by living things to help speed up chemical reactions 2. Enzymes A function at any temperature and pH B function at an optimum temperature and pH C function at a temperature of 98.6F and a pH of 7 D function at a temperature of 96.8F and a pH of 1-14 Levels of organization: Celltissueorganorgan system Muscle cellheart muscleheartcirculatory system 1. A ______________ is a group of different tissues that work together to perform a certain function A organ system B organ C cell D tissue 2. Which of the following is part of the cell theory? A are eukaryotic B are prokaryotic C have nuclei D come from other cells Objective 2.01-Biomolecules Biomolecule Building Block Elements Function Examples Carbohydrate Monosaccharide (simple sugar) Disaccharides Polysaccharides Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen Primary (fast) Sugar, source of energy starch Lipid Fatty acids (insoluble in water –hydrophobic) Carbon, hydrogen Insulation, protection, long term energy source Oil, wax Protein Amino Acids (held together by peptide bonds) Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen Growth and repair of tissues Speed up reactions enzymes Nucleic Acids Nucleotides Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus Carries hereditary information DNA/RNA Cool-Down Name one part of the cell theory. What is the subunit (building block) of proteins? Of carbohydrates?