* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organism of the Day: Cheetah
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
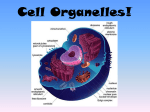
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Organism of the Day: Cheetah Acinonyx jubatus Ancient Egyptians tamed Cheetahs and kept them as pets. Cheetahs can reach speeds of 70 to 75 mph, making it the fastest land animal. Cheetahs can accelerate from 0 to 63 mph in 3 seconds! Very low genetic variability among cheetahs. This is thought to be due to a bottleneck during the last ice age. 1. How do large lungs enable a Cheetah to move at high speeds? 2. What organelle uses oxygen and is known as the powerhouse of the cell? 1 Biology Tuesday/Wednesday December 4/5, 2012 1. Organism of the Day 2. Review Notes on Cells 3. Continue Notes on Cells 4. Begin Cell Story Project Announcements Due Thursday/Friday, December 4/5: Read 7.2 and answer questions 1 5 2 Two Cell Types Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 3 Prokaryotes = Bacteria (mostly) CHARACTERISTICS • Simple • Small • Cell membrane and cell wall • No membrane bound organelles but do have ribosomes. • Have DNA, but not in a nucleus 4 What bacteria Do: • Autotrophs • Produce oxygen • • • • • Fix nitrogen Recycle nutrients Form antibiotics Help in digestions/formation of vitamins Production of cheese and yogurt 5 Two Cell Types Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 6 Eukaryotes Characteristics 1. More complex 2. Larger 3. Cell membrane. 4. Membrane bound organelles 5. DNA in nucleus 7 PARTS OF EUKARYOTIC CELLS • Cell wall • • • • • • • • • • Cell membrane Lysosomes Mitochondria Nucleus Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Cytoskeleton Microtubules Cilia Know These!!! 8 Cell Wall Support and protects plant and fungi cells. Made of cellulose in plants and chitin in fungi Plasma Membrane Controls what comes in/out of a cell. 9 Eukaryotes Organelles are important in keeping non compatible reactions separate, yet allowing them to happen at the same time! 10 Endocytosis 11 Lysosomes Contain enzymes to break down food brought in by endocytosis; can also break down own molecules for recycling. 12 Mitochondria Break down food to produce adenosine triphosphate, ATP. ATP provides the cell with an accessible source of energy. Can you name a functional group in ATP? 13 Nucleus Contains chromosomes which are DNA wrapped around protein spools. Also contains nucleoli, which are areas where rRNA and tRNA are made. 14 Ribosomes Synthesize proteins 15 Endoplasmic Reticulum A system of tubes that carry proteins to destinations in the cells and alters proteins as they move. 16 Golgi Apparatus Where proteins from the ER are further refined and packaged for final transport. 17 Vacuoles Found in both plant and animal cells; store water, digestive enzymes, salts, pigments, etc. 18 Cytoskeleton A network of protein fibers that help the cell keep its shape and helps things move around (like a freeway). 19 Eukaryotic Cells 20 Cell Story Project 21 Exit Questions: Identify one difference between plant and animal cells. Reminders: Due Thursday/Friday December 6/7: Read 7.2 and answer questions 1 5. ` 22