* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Four Stages of Mitosis
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
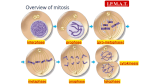
By: Bobby Naugle Sophie Terry Krista Pipan Prophase Telophase Mitosis Anaphase Metaphase Means in Ancient Greek “before stage” Chromatin condenses into a structure called chromosome which is called Chromatin condensation Sister chromatids are attached to each other at the centromere The centrosomes move away from each other, apparently propelled by the lengthening microtubules between them The nuclear envelope breaks down and microtubules of the spindle fiber can now invade the nuclear area and interact with the chromosomes, which have become more dense Each of the two chromatids of a chromosome now has a kinetochore “Kinetochore Microtubules” jerk the chromosomes back and forth Nonkinetochore microtubules interact with those from the opposite pole of the spindle SWEET PICS ANIMAL PLANT In Greek it means “between stage” The longest stage of mitosis , lasting about 20 minutes. The centrosomes are now at the opposite ends of the cell The chromosomes are located in the middle of the cell on the metaphase plate where they are equidistant from the chromosomes on each end of the cell SWEET PICS ANIMAL PLANT In Greek means “up stage” The shortest of the stages, lasting only a few minutes The sister chromatids of each pair suddenly part, making each chromatid a chromosome As kinetochore microtubules shorten the chromosomes are pulled to opposite ends of the cell The cell elongates as the nonkinetochore microtubules lengthen As anaphase ends the two ends of the cell have equivalent and complete collections of chromosomes SWEET PICS ANIMAL PLANT Two daughter nuclei begin to form in the cell The nuclear envelopes arise from the fragments of the parent cell’s nuclear envelope and other portions of the endomembrane system The chromosomes become less condensed Mitosis is complete SWEET PICS ANIMAL PLANT Centrosomes- small region of cytoplasm adjacent to the nucleus that contains the contrioles and serves to organize microtubules Endomembrane system – composed of the different membranes that are suspended in the cytoplasm within a eukaryotic cell Kinetochores – protein structure on chromosomes where the spindle fibers attach during division to pull the chromosomes apart Metaphase plate – plane of the equator of the spindle into the which chromosomes are positioned during metaphase Spindle fibers – microtubules that move chromosomes during cell division http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/1110Lab/n otes/notes1/labpics/lab6pics.htm http://www.accd.edu/sac/biology/MrT/0 6web3/CH12.html http://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourse s/N100/2k2ch8mitosis.html http://biog-101104.bio.cornell.edu/biog101_104/tutorial s/cell_division/onion_review_fs.html