* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lec.14 Dr:Buthaina Al-Sabawi Date:21/12/2016 Mitosis
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
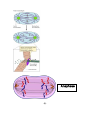
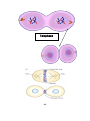
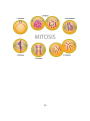
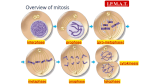
Events during Mitosis Lec.14 Dr:Buthaina Al-Sabawi Date:21/12/2016 Mitosis Mitosis is a process where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells (cell division). During mitosis one cell divides ONCE to form two identical cells. The major purpose of mitosis is for growth and to replace worn out cells. Mitosis is nuclear division plus cytokinesis, and produces two identical daughter cells during prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Interphase: Cells may appear inactive during this stage, but they are quite the opposite. This is the longest period of the complete cell cycle during which DNA replicates, the centrioles divide, and proteins are actively produced. For a complete description of the events during Interphase, read about the Cell Cycle. Interphase Prophase: Chromosomes become more coiled and can be viewed under a light microscope. Each duplicated chromosome is seen as a pair of sister chromatids joined by the duplicated but unseparated centromere. (1) The nucleolus disappears during prophase. In the cytoplasm, the mitotic spindle, consisting of microtubules and other proteins, forms between the two pairs of centrioles as they migrate to opposite poles of the cell. The nuclear envelope disappears at the end of prophase. This signals the beginning of the substage called prometaphase. Prophase Prometaphase: In this stage the nuclear envelope breaks down so there is no longer a recognizable nucleus. Some mitotic spindle fibers elongate from the centrosomes and attach to kinetochores, protein bundles at the centromere region on the chromosomes where sister chromatids are joined. Other spindle fibers elongate but instead of attaching to chromosomes, overlap each other at the cell center. Metaphase: The chromosomes become arranged on the metaphase plate and are attached to the now fully formed spindle. (2) (3) Kinetochore microtubules: each sister chromatid is attached to a kinetochore microtubule; in cell division during anaphase the microtubules hold onto the kinetochore and pull the two sister chromatids apart to opposite poles. Polar microtubules: microtubules that connect to each other from opposite poles; by pushing against each other they elongate the cell; during anaphase they disconnect and are pulled apartd. Aster microtubules: microtubules that extend to the top of the cell; above the centrosome; during prophase they start extending into polar microtubules. Anaphase: Spindle fibers shorten, the kinetochores separate . Anaphase begins when the duplicated centromeres of each pair of sister chromatids separate, and the now-daughter chromosomes begin moving toward opposite poles of the cell due to the action of the spindle. At the end of anaphase, a complete set of chromosomes has assembled at each pole of the cell. (4) Telophase: Chromatids arrive at opposite poles of cell, and new membranes form around the daughter nuclei. The chromosomes disperse and are no longer visible under the light microscope. The spindle fibers disperse, and cytokinesis or the partitioning of the cell may also begin during this stage. Cytokinesis: In animal cells, cytokinesis results when a fiber ring composed of a protein called actin around the center of the cell contracts pinching the cell into two daughter cells, each with one nucleus. In plant cells, the rigid wall requires that a cell plate be synthesized between the two daughter cells. Anaphase (5) Telophase (6) (7)