* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELLS, CELLS, & More CELLS!
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
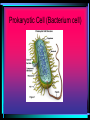
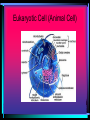
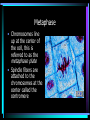
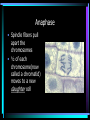
CELLS, CELLS, & More CELLS! The Cell Theory • Cells are the fundamental building blocks of life • All living creatures are made up of cells • Cells come from pre-existing cell The adult human body is made up of about 60-90 trillion cells. (if you lined up all the cells in a human body end-to-end, you could actually circle the earth 4.5 times.) Bone Cell Brain Cell Stomach Cell Red Blood Cell “TO HAVE OR NOT TO HAVE” That is the question! • PROKARYOTIC CELL • Organisms whose cells DO NOT have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles • EUKARYOTIC CELL • Organisms whose cells DO have a nucleus & membrane bound organelles Prokaryotic Cell (Bacterium cell) Eukaryotic Cell (Animal Cell) Why are cells so small? Cells are small because…… • Diffusion of necessary materials is quicker & more efficient when cells have a large surface area/volume ratio • Allows for continual renewal of cells without interruption of entire organism Conquering the GREAT DIVIDE Cell Division (Mitosis) Why do organisms need new cells? • Cell damage/death • Limited life span • Cells get too large to survive (SA:V ratio) The Cell Cycle • Each round of growth & division in a cell is a cell cycle • G1-Cells grow • S-Cell materials doubles • G2-final prep for division • Mitosis The Stages of Mitosis remember “IPMAT” • Interphase-technically not a phase of Mitosis but a stage of the Cell Cycle • Prophase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telophase Prophase • Chromosomes in the nucleus coil and thicken • The nucleolus disappears • Centrioles move to opposite ends of cell and spindle fibers form Metaphase • Chromosomes line up at the center of the cell, this is referred to as the metaphase plate • Spindle fibers are attached to the chromosomes at the center called the centromere Anaphase • Spindle fibers pull apart the chromosomes • ½ of each chromosome(now called a chromatid) moves to a new daughter cell Telophase • Chromatids arrive at opposite poles of cell • Chromatids DECONDENSE • Cytokinesis begins-Cell membrane begins to pinch to form two new identical daughter cells