* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation1
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Orbitofrontal cortex wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Diffusion of innovations wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
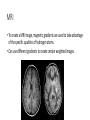
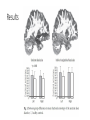
Frontoemporal white-matter microstructural abnormalities in adolescents with conduct disorder. Sarkar et al. (2013) MRI • To create a MRI image, magnetic gradients are used to take advantage of the specific qualities of hydrogen atoms. • Can use different gradients to create certain weighted images. It’s all about Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) • Diffusion = movement of fluid or gas. • Water normally diffuses randomly- isotrpic. • But in the brain water movement is constrained by the structure of cells axons, like water being pushed through a straw. • So we can exploit the non-random (anisotropic) nature of water movement to map out these fibres. • Yes we can. But how… • DTI uses MRI (as it’s structural) but the MR signal is now dependent on diffusion rather than grey or white brain matter. • Allows researches to look at the connections, wiring, between brain regions. http://www.patient.co.uk/doctor/magnetic-resonance-imaging Diffusion tensor MR imaging of the brain and white matter tractograhpy, melhem et al. (2002). The research • Children with Conduct disorder are at increased risk of developing antisocial personality disorders. • And there’s a strong correlation with substance abuse. • fMRI studies have reported reduced volumes in the prefrontal cortex (linked to reduce self-control). • Yet, the brain is a system and crucial to understand the connections between the brain. The Uncinate Fasciulus (UF) • This is a white matter tract (a straw) that connects the amygdala and the orbitofrontal cortex. • Past studies have shown that in children with Anti Social Personaility Disorder the UF is damaged, with reduced diffusion through the tract. The big question • UF damage seems to be linked to antisocial behaviour. Would this be the case for children with conduct disorder when compared against peers? • And if so, there should be reduced diffusion through the UF. Method • Participants (27 conduct disorder and 16 controls, aged 12-19). • As a structural experiment participants just sat in the scanner. • Used a eight-channel head coil to speed up imaging. • And luckily the scan only took 15min. • Also completed a battery of tests measuring anti-social behaviour. Data pre-processing • Each image was inspected visually for motion artefacts etc. • Datasets showing significant movement (> 1 cm) were removed. • Performed further pre-processing to correct and tease out diffusion tensor. DTI • To define the area of the UF a region of interest approach was used. With trained operators dissecting the images by hand. • Operators were blind to the clinical groupings. • Had a defined area by placing the first and second ROI in a specific space. • Long tracts that extended outside frontal and temporal lobes were excluded as were short tracts that didn’t enter the fixed ROI’s. Results • Data analysed using SPSS. • Repeated-measures analysis was used to test for differences in diffusion between the clinical and control groups. • Used the Bonferroni method to correct for multiple comparisons. Results • The Conduct Disorder group had significantly greater diffusion in the left UF than controls. • Also had greater diffusion in the right UF, but this did not withstand the correction. • There was also a significant correlation between the left UF abnormality and high anti-social scores. • But no significant differences in a control tract. Results Discussion • So, children with conduct disorder have significantly different connectivity than controls. • No differences in control tract suggest no global connection impairment. • So result support hypothesis that antisocial behaviour is associated with abnormal connectivity in limbic connections, rather than global changes. • Indicates a biological mechanism for conduct disorder traits. Discussion • However, change was in the opposite direction to the hypothesis, increased diffusion. • Post-hoc explanation argued that alternated connectivity of the OFC and the amygdala secondary to the observed changes in the UF might lead to behavioural disinhibition seen in the clinical group. • Chicken and the egg question as with the experimental design it is impossible to say how these abnormalities arise, or if they predict outcome. Take home message • Research used DTI to map the UF tract in children with conduct disorder and controls. • The authors found that there was a significant difference, with the clinical group having greater diffusion (counter to the hypothesis) through the UF. • Unclear why or what effect this has on conduct disorder. But there is an effect.