* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Physiology
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
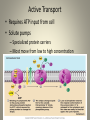
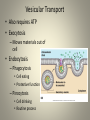
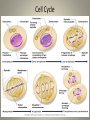
Cell Physiology Cell Physiology • Most cells have the ability to: – Metabolize – Digest foods – Dispose of wastes – Reproduce – Grow – Move – Respond Membrane Transport • Cell membrane is selectively permeable • Passive Transport – No energy input from the cell • Active Transport – Requires energy from the cell Passive Transport • Diffusion – Movement from high to low concentration – Molecule requirements • Small Simple diffusion • Lipid soluble • Have a membrane carrier Facilitated diffusion – Osmosis • Diffusion of water – Filtration • Force by pressure not concentration • High pressure to low pressure Active Transport • Requires ATP input from cell • Solute pumps – Specialized protein carriers – Most move from low to high concentration Vesicular Transport • Also requires ATP • Exocytosis – Moves materials out of cell • Endocytosis – Phagocytosis • Cell eating • Protective function – Pinocytosis • Cell drinking • Routine process Cell Life Cycle • Results in identical daughter cells • Consists of interphase and cell division • Interphase – Longer phase, preparations to divide • Cell division – Mitosis • Division of the nucleus – Cytokinesis • Division of the cytoplasm Cell Cycle Protein Synthesis • Proteins are essential to cell life • Two major processes – Transcription • Occurs in nucleus • DNA is transcribed into mRNA – Translation • mRNA moves from nucleus • mRNA translated into proteins – tRNA transfers amino acids – Ribosome assembles protein