* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What are all living things composed of?
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
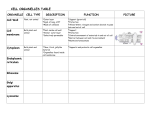
List some common foods that are high in protein, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Agenda for Monday Nov 7th 1. Cell theory 2. Organelle Posters Cell Theory Robert Hooke • Made simple microscope • Looked at cork – observed small box like structures – Called them cellulae (small rooms) = cells Cell Theory Anton van Leewenhoek • Created a microscope • Saw living things in milk, pond water, etc Matthias Schlieden • Looked at plants and concluded they were composed of cells Theodore Schwann • Animals composed of cells Rudolph Virchow • All cells come from existing cells Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and organization of all living organisms 3. Cells arise only from previously existing cells 1. Cells pass on copies of their genetic material to their daughter cells List the 3 parts to the cell theory. Agenda for Tuesday Nov 8th 1. Finish posters 1. Present 2. Cell organelle book/worksheet 3. Cell organelle Notes Organelle Posters • • • • • • Cell Theory Mitochondria Nucleus Ribosome Vacuole Endoplasmic Reticulum • • • • • • • Cell Wall Centriole Chloroplast Cilia/flagella Cytoskeleton Golgi Apparatus Lysosome/peroxisome List one fact about your organelle. Agenda for Wednesday Nov 9th 1. Go over organelles 2. Coloring 3. Cell city analogy Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic ** Organelles – specialized structures in cells that carryout specific functions Prokaryotic Cells • Prokaryotes • Small and simple • Circular DNA • No nucleus or membrane bound organelles • Usually unicellular – Bacteria Eukaryotic Cells • Eukaryotes • Higher level organisms and function • Most organisms (plants, animals) are made up of eukaryotic cells • Nucleus –organelle that contains DNA (linear) – Other membrane bound organelles Plant Cell Animal Cell Organelles in the Cell • Plasma membrane – Controls what enters and leaves cell – Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells • Cytoplasm - Liquid within the cell • Cell Wall – plants and fungi – support and protect the cell – Plants’ = cellulose Fungi = chitin Organelles • Nucleus - contains DNA – DNA – instructions needed to produce proteins • Chromatin • Nucleolus – within nucleus – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) • Nucleoplasma – liquid within nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum • Single, continuous membrane • Pipes, tubes and tunnels in cell – Superhighway of the cell • 2 kinds: Rough ER + Smooth ER – Rough ER - Studded, or covered, with ribosomes • Ribosomes – site of protein synthesis Golgi Apparatus • Store, package, sort and modify proteins – The UPS of the cell Vesicles and Vacuoles Vacuoles • Store material • Not usually found in animal cells Lysosomes &Peroxisomes • Contain digestive enzymes • Breakdown cell's food and wastes Mitochondria • Produces energy for the cell – Cell's "power house“ – Converts sugars into energy (ATP) • Composed of 2 membranes Chloroplasts • Found only in green plant cells and algae • Site of photosynthesis – Use the sun’s energy and convert to chemical energy • Contain pigment chlorophyll Cilia/Flagella • Cilia – all over cell, smaller, aid in movement of cell • Flagella – longer projections, aid in movement of cell Other cell parts Cytoskeleton • Framework inside cell • Support and movement • Composed of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules Centrioles • Aid in cell division • Found only in animal cells Plant vs. Animal Cell Plant Cells • Cell Wall – And cell membrane • Chloroplasts • Large vacuoles Animal Cells • No Cell wall – Cell membrane only • No Chloroplast • Small or absent vacuoles All other organelles are the same in each cell