* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download daughter DNA interphase volume binary fission G1 nucleus cell
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
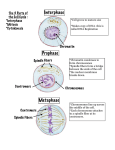
During interphase, there are three stages. During the __________ phase, the cell grows. During the ___________ phase, the genetic material (DNA) of the cell is copied. During the ____________ phase, the cell prepares for division. The events that make up the life of a cell are called the _________________. The two main parts of this cycle are ___________________ and ___________________. Each chromosome has two identical sections of DNA called ______________ that are connected at a region called the _____________________. These identical sections of DNA must separate during cell division. Uncoiled DNA and proteins are called ____________________, which coils up during cell division to form ____________________. In eukaryotic cells, cell division is a little more complicated. In these cells, DNA is found in the ____________. During prokaryotic cell division, DNA is copied and divided into two identical ____________ cells. This process is called ______________________. Another reason cells cannot grow forever is that the _______________ of their membrane does not increase as quickly as the ________________, which limits the necessary transport of materials into and out of the cell. To make large organisms (ex: plants and animals), cells divide because they can’t continue to grow forever. One reason they can’t grow forever is they will not have enough __________ to control a massive cell’s activities. daughter DNA interphase volume binary fission G1 nucleus cell cycle chromatin chromatids centromere S chromosomes cell division G2 prophase mitotic spindle cleavage furrow metaphase mitosis nuclear membrane anaphase centromere cytokinesis telophase centrioles cell plate surface area After mitosis, the cytoplasm divides in a process called cytokinesis. In animal cells, the cell membrane pinches in to form a __________________. In plant cells, a _________________ forms between the two new daughter cells. During ____________________, two nuclear membranes reform, chromosomes uncoil, and the mitotic spindle breaks down. At this point, nuclear division is complete. During ___________________, spindle fibers pull apart chromatids and carry new daughter chromosomes to opposite ends of the dividing cell. During ___________________, spindle fibers arrange chromosomes at the center of the cell along a line called the metaphase plate. Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes at the ___________________. In this stage, the ________________________ also begins to form when proteins called microtubules grow from structures at either end of the cell called _______________________. During _________________, the _____________________ breaks down and chromatin coils into chromosomes. Cell division involves two parts, mitosis and cytokinesis. _______________ is division of the nucleus, and _______________ is division of the cytoplasm.