* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
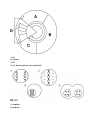
Study Guide Cell Division and Growth Limits to Cell Growth DNA “overload” as cell grows, more demand is placed on DNA Exchanging materials as cell grows, exchange of materials across membrane is harder because food and oxygen is being used quicker Ratio of surface area to volume volume increases 100 times faster than the surface area The Cell Cycle- series of events a cell goes through to grow and divide; creating an exact replica of parent cell; occurs when cell has reached it’s full growth when growth and/or repair is necessary In prokaryotic cells- (unicellular organisms) binary fission In eukaryotic cells- (multicellular organisms) Structure of a chromosome made of DNA molecules, when tightly condensed looks like an “X” (chromatids attached by a centromere) (know correct order, what happens at each step and how to identify pictures/slides) Interphase (Cell Growth) cell grows, duplicates organelles, and copies DNA G1 cell growth S phase DNA replicates G2 prepares for mitosis Mitosis (Cell Division) visible chromosomes Prophase chromosomes visible Metaphase chromosomes line up at equator M phase Anaphasechromosomes split at centromere;chromatids move toward poles Telophase nuclear envelope forms; cleavage begins Cytokinesis division of cytoplasm; daughter cells formed Checkpoints- kinases (CDK) and cylcins-proteins that control the cell cycle from moving from one stage to the next Controlling Cell Division Cell cycle regulators internal and external factors, contact with other cells Cancer uncontrolled cell division o Malignant tumors cancerous, can spread throughout body o Benign tumors non cancerous, can be removed through surgery, does not spread Levels of organization celltissueorganorgan systemorganism Cell Specialization perform specific functions (example-blood cells carry gases and nutrients) Stem cells have the ability to divide and renew themselves, capacity to differentiate, develop into specialized cell types adult hard to isolate and grow vs embryonic are pluripotent and can be grown indefinitely in culture pluripotent can grow into any cell type except totipotent (from embryonic stem cell) Mulipotent can grow into cells of a closely related family (from adult stem cell) Totipotent can grow into any other type of cell (fertilized egg from a new organism) made of 2 chromatids connected by a centromere A-G1 B-S phase C-G2 D-cell division (mitosis and cytokinesis) A-anaphase B-prophase C-metaphase D-telophase Look over your notes and EW questions!!!!!!