* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Division
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
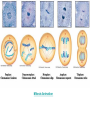
Mitosis Chapter 10 What Are Chromosomes? • Strands of DNA • Every organism has a specific number of chromosomes • Before cell division occurs, DNA must be copied so each new cell will have DNA. • Once copied, the two identical strands (or CHROMATIDS) are held together by a CENTROMERE.. Cell Cycle – “Life of a Cell” • Interphase – growth period of cell, longest stage of cell life. 1. G1 phase – growth, more organelles 2. S phase – DNA duplication 3. G2 phase – preparation for mitosis • Cell Division – division of the cell into 2 1. Mitosis – division of the nucleus 2. Cytokinesis – division of the cytoplasm Section 10-2 The Cell Cycle G1 phase M phase S phase G2 phase Mitosis = Cell Division • Prophase – cell prepares to be divided; chromatin condenses, centrioles separate to opposite sides of cell (animal cells only), spindle forms, nuclear membrane breaks down • Metaphase – Chromosomes line up in middle • Anaphase – sister chromatids separate apart • Telophase – new nuclear membranes form and begin to tear the cells in two Cytokinesis Division of the cytoplasm Differences in Cell Division: 1.In animal cells: cleavage of cell membrane 2.In plant cells: a cell plate forms midway between the divided nuclei Mitosis Animation What happens if something goes wrong with the cell cycle? Cancer • Uncontrolled cell division • DNA is damaged by carcinogens or genetically inherited • Cell will not respond to cell cycle regulators • Carcinogens can be radiation or chemicals Tumor Stem Cells • Cell that have not become specialized. • Stem cells can become any type of human cell. Abundant in embryos. • Possible uses in science: treating nerve damage, growing organs, treating diseases.