* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organization of the Nervous System
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
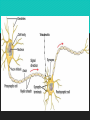
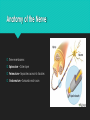
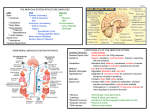
Organization of the Nervous System Exercise 18 Main Responsibilities Detect changes in and around the body Process incoming sensory information and react accordingly Orchestrate and integrate all sensory and motor activities Ultimate goal maintain homeostasis CNS vs. PNS Central Nervous System (CNS) brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) communicates with CNS via cranial and spinal nerves Peripheral Nervous System Afferent Division RECEIVES sensory information and then sends the information to the CNS for processing Motors responses are generated and PNS carries our the demands via the…. Efferent Division CARRIES OUT the responses to sensory information Controls the activities of “effectors” (muscles and glands of the body) Somatic Nervous System (conducts motor responses to skeletal muscles) Autonomic Nervous System (sends commands to the visceral effectors) Sympathethic Parasympathetic PNS Nerves Cranial Nerves Communicate with the brain Pass into neck and face through the foramina in the skull Spinal Nerves Join spinal cord at intervertebral foramina Pass into upper and lower limbs of the body “Mixed” – carry BOTH sensory and motor signals A Closer Look @ Nervous System Cells GLIAL CELLS– support, protect, and maintain nerve tissue Most abundant cells in the nervous system CNS production and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 2 types (PNS) Satellite Cells Schwann Cells 4 types (CNS) Oligodendrocytes form myelin sheath Microglia remove microbes and cellular debris from CNS tissue Ependymal line the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord Astrocytes maintain the blood brain barrier (BBB), structural support, regulate ion content, and repair A Closer Look @ Nervous System Cells NEURONS - communication cells Components: dendrites, cell body, axon Nissl bodies: groups of free ribosomes and RER Telodendriad Anatomy of the Nerve Three membranes: Epineurium – Outer layer Perineurium – Separates axons into fassicles Endoneurium – Surrounds each axon https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TKG0MtH5crc Extra Credit – 5 BP towards exam Chapter 13 OR Chapter 7