* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Repetition Summary of last lecture Energy Cell Respiration
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
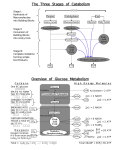
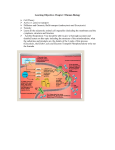
3/29/16 Energy flowsintoanecosystemassunlightandleavesitasheat Light ener gy Repetition ECOSYSTEM Summary of last lecture Photos y nthe s is i n c h l o ro p l as ts CO2 + H2O Ce llula r re s pira tion i n mi to c h o n d ri a Org a n i c + O2 mo l e c u l e s ATP pow er s m ost cel l ul ar w or k Heat ener gy Aerobic oxidation of pyruvate and fatty acids in mitochondria Cell Respiration There are three mainprocessesinthismetabolicenterprise CYTOSOL El e c tro n sh uttle s s p a n me mb ra ne MITOCHONDRION 2 NADH or 2 FADH2 2 NADH 2 NADH Gly c oly s is Gl u c o s e 2 Py ru v a te 2 Acet yl CoA + 2 ATP b y s u b s tra te-l e ve l p h o s p h o ry l ati on Ma x i mu m p e r g l u c o s e: 6 NADH Citric a c id c y c le 2 FADH2 O xi dat i ve phosphor yl at i on: el ect r on t r anspor t and chem i osm osi s + 2 ATP + a b o u t 3 2 o r 34 ATP b y s u b stra e t -le ve lb y o x i d ati ve p ho sp ho ryl ati on , d ep en di n g phos phoy ra l tio n o n wh i c h sh uttle tra ns po rts e l ectro ns fro m NADH i n c yto so l Ab o u t 3 6 o r 3 8 ATP The out er m em br ane is f r eely per m eable t o all m et abolit es, but specif ic t r anspor t pr ot eins ( color ed ovals) in t he inner m em br ane ar e r equir ed t o im por t pyr uvat e ( yellow) , ADP ( gr een) , and Pi ( pur ple) int o t he m at r ix and t o expor t ATP ( gr een) . NADH gener at ed in t he cyt osol is not t r anspor t ed dir ect ly t o t he m at r ix because + + t he inner m em br ane is im per m eable t o NAD and NADH; inst ead, a shut t le syst em ( r ed) t r anspor t s elect r ons f r om cyt osolic NADH t o NAD in t he m at r ix. O 2 dif f uses int o t he m at r ix and CO 2 dif f uses out . St age- 1: special car r ier ( blue oval) and t hen r eat t ached t o CoA • About 40% of the energy in a glucose molecule is transferred to ATP during cellular respiration, making approximately 38 ATP ( at t ached t o CoA) ar e also conver t ed t o acet yl CoA f at t y acyl gr oups ar e t r ansf er r ed f r om f at t y acyl CoA and t r anspor t ed acr oss t he inner m em br ane via a on t he m at r ix side. Pyr uvat e is conver t ed t o acet yl CoA wit h t he f or m at ion of NADH, and f at t y acids wit h f or m at ion of NADH and FADH2. O xidat ion of acet yl CoA in t he cit r ic FADH2. St age- 2: elect r ons f r om t hese r educed coenzym es ar e t r ansf er r ed via elect r on t r anspor t com plexes ions f r om t he m at r ix t o t he int r am em br ane space, gener at ing t he pr ot on- m ot ive f or ce. Elect r ons f r om NADH com plex ar r ows I I . St age 3: ATP synt hase, t r ansm em br ane m ovem ent t he F0F1 com plex ( or ange) , of pr ot ons; and gr een ar r ows har nesses indicat e t he pr ot on- m ot ive t r anspor t acid cycle gener at es NADH and + ( blue boxes) t o O 2 concom it ant wit h t r anspor t of H f low dir ect ly f r om com plex I t o com plex I I I , bypassing f or ce t o synt hesize ATP. Blue ar r ows indicat e elect r on f low; r ed of m et abolit es. 1 3/29/16 TypesofFermentation 2 ADP + 2 P1 2 ATP (ATP without the use of oxygen) • Fermentationconsists of G lucose C 2 ADP 2 Acet aldehyde + 2 P1 O C C Am ino O– 2 NADH C O C O Sugar s G lycer ol Fat t y acids G l ycol ysi s Funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules into cellular respiration – Fat s Car bohydr at es acids • Catabolic pathways 2 ATP G lycolysis 2 NAD+ H TheVersatility ofCatabolism f er m ent at i on G lucose • During lactic acid fermentation CO 2 O CH3 ( a) Al cohol • In alcohol fermentation 2 H OH CH3 pyruvate is reduced directly to NADH to form lactate as a waste product Pr ot ei ns 2 NADH H C 2 Et hanol – O 2 Pyr uvat e 2 NAD+ H pyruvate is converted to ethanol in two steps, one of which releases CO 2 O C CH3 • - glycolysis plus reactions that regenerateNAD +, which canbe reused byglyocolysis – • Glycolysisandthecitricacidcycleconnecttomany othermetabolicpathways O – C G lycolysis Gl u c o s e G lycer aldehyde- 3- NH3 P Py ru v a te • The catabolism of various molecules from food Acet yl CoA Ci t r i c CH3 aci d cycl e O OH CH3 2 Lact at e O xi dat i ve phosphor yl at i on ( b) Lact i c aci d f er m ent at i on • Steroid hormonesbindtointracellular receptors Cell Signalling – HormoneSignalling (a ligand) Ho rmo n e (te s to s tero ne ) EXTRACEL LU LA R FLUI D Pl a s ma me mb ra n e 1 The steroid hormone testosterone passes through the plasma membrane. 2 Testosterone binds to a receptor protein in the cytoplasm, activating it. Re c e p to r p ro te i n Ho rmo n e re c e p to r c o mp l e x 3 The hormone- receptor complex enters the nucleus and binds to specific genes. DNA 4 mRNA NUCL EUS The bound protein stimulates the transcription of the gene into mRNA. Ne w p ro te i n 5 The mRNA is translated into a specific protein. CYTOPL ASM 2 3/29/16 1 CellSignalling – ReceptorsinthePlasmaMembrane Signalling • maintypesofmembranereceptors A signal m olecule t o a r ecept or , leading Calcium act ivat ion 2 binds to of phospholipase Phospholipase plasm a C. EXTRACEL L UL AR FL UID called C cleaves 3 a DAG f unct ions as a second m em br ane phospholipid PI P2 int o DAG m essenger in ot her pat hways. and I P3. Si g n a l mo l e c u e l (fi rs t me s s e n g er) G p ro te i n DAG (d i a c y l g l yc e rol ) G TP PIP2 G-p ro te i n -l i n k e d re c e p to r • G-protein-linked Ph o s p h o l i p as e C I P3 ( second m essenger ) IP3-g a te d c a l c i u m c h a nn e l • Tyrosinekinases En d o p l a s mi c re ti c u l u m (ER) • Ion channel Va ri o u s p ro te i n s a c ti v a te d Ca 2+ Ce l l u l a r re s p o n s e Ca 2+ (s e c o n d me s s e n g e r) 4 I P3 quickly dif f uses t hr ough t he cyt osol and binds t o an I P3– gat ed calcium m em br ane, Gro wth fa c to r • Other pathways • regulategenes byactivating transcription factorsthat turn geneson or off Re c e ption Re c e p to r channel causing in t he ER it t o open. • Ionchannelreceptors 5 6 Calcium o i ns f low out of t he ER ( down t heir con- The calcium act ivat e t he next cent r at ion gr adient ) , r aising 2+ t he Ca level in t he cyt osol. Si g n a l mo l e c u l e (l i g a n d ) Ga te c l o s e d L i g a n d -g a te d i o n c h a n n e l re ce p to r Ph o s p h o ryl ati on c as c ade ions pr ot ein n i one or m or e signaling pat hways. Io n s Pl a s ma Me mb ra n e Tra ns duc tion Ga te o p e n CYTOPL ASM In a c ti v e tra n s c ri p ti o n fa c to r Ac ti v e tra n s c ri p ti o n fa c to r Ce l l u l a r re s p o n s e P Re s pons e DNA Ga te c l o s e Ge n e NUCL EUS mRNA 3