Lack of Knowledge on the Use and Benefits of Creatine
... when certain sports require dehydration, for example like wrestling. Furthermore, more ASOS mentions that it is dangerous for someone who is trying to lose weight. This is because, water will be retained, which increases weight, and not decrease it. Plus, an increased water weight will keep the fact ...
... when certain sports require dehydration, for example like wrestling. Furthermore, more ASOS mentions that it is dangerous for someone who is trying to lose weight. This is because, water will be retained, which increases weight, and not decrease it. Plus, an increased water weight will keep the fact ...
Safety Assessment of Centella asiatica
... asiaticin (p-benzoyloxy methyl-butyl benzoate) centellicin (1-(2',3'-dihydroxypropyl)-2-en-3-methyl-6-hydroxy-9-yn-undecanoate) ...
... asiaticin (p-benzoyloxy methyl-butyl benzoate) centellicin (1-(2',3'-dihydroxypropyl)-2-en-3-methyl-6-hydroxy-9-yn-undecanoate) ...
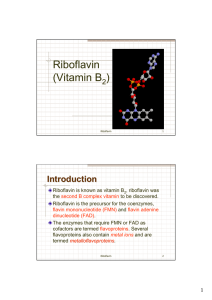
Riboflavin (Vitamin B )
... Riboflavin is instrumental in cell respiration, helping each cell utilize oxygen most efficiently. FMN & FAD operate in pyridine nucleotidedependent and independent dehydrogenations, reactions with sulfur-containing compounds, hydroxylation, oxidative decarboxylation, deoxygenation, and reduction of ...
... Riboflavin is instrumental in cell respiration, helping each cell utilize oxygen most efficiently. FMN & FAD operate in pyridine nucleotidedependent and independent dehydrogenations, reactions with sulfur-containing compounds, hydroxylation, oxidative decarboxylation, deoxygenation, and reduction of ...
Carnitine-Metabolism and Functions
... This enzyme (EC 1.14.11.-) is a dioxygenase localized in the mitochondria of kidney, liver, heart, skeletal muscle, and probably other tissues (389). The enzyme requires a-ketoglutarate and oxygen as cosubstrates and ferrous ions and ascorbic acid for optimal activity (203). The enzyme presumably ha ...
... This enzyme (EC 1.14.11.-) is a dioxygenase localized in the mitochondria of kidney, liver, heart, skeletal muscle, and probably other tissues (389). The enzyme requires a-ketoglutarate and oxygen as cosubstrates and ferrous ions and ascorbic acid for optimal activity (203). The enzyme presumably ha ...
Creatine A Complete Users Guide
... from food by our bodies. It provides the energy muscles need to move and is often used by athletes to improve their sports performance. Fair Trading Director Deborah Battell said that in the Commission's view, Muscle Marketing USA falsely represented that 5ml of its serum yielded the equivalent of 2 ...
... from food by our bodies. It provides the energy muscles need to move and is often used by athletes to improve their sports performance. Fair Trading Director Deborah Battell said that in the Commission's view, Muscle Marketing USA falsely represented that 5ml of its serum yielded the equivalent of 2 ...
(Book) Creatine: Increasing Sports Performance
... Shortly thereafter, U. S. champion athletes began using creatine. Since then, scientists have elucidated more Asecrets@ on how to best utilize creatine for optimal benefit. Now champion athletes from most countries are using creatine supplements. The list of U. S. athletes is a AWho=s Who@ in track ...
... Shortly thereafter, U. S. champion athletes began using creatine. Since then, scientists have elucidated more Asecrets@ on how to best utilize creatine for optimal benefit. Now champion athletes from most countries are using creatine supplements. The list of U. S. athletes is a AWho=s Who@ in track ...
No Slide Title
... • 1963: 2 adults, aged 33 and 39 years were identified with the same condition. In addition to the aversion to fructose-containing ...
... • 1963: 2 adults, aged 33 and 39 years were identified with the same condition. In addition to the aversion to fructose-containing ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... The action of ammonia furnishes a carboxamide R1–CO–NH2 via an ammonolysis reaction [15, 16]. An incoming amine R3–NH2 results in the formation of an N-substituted amide R1–CO–NH–R3, yielding an enzymatic aminolysis of esters [17, 18]. Peracids of type R1–CO–OOH are formed when hydrogen peroxide is ...
... The action of ammonia furnishes a carboxamide R1–CO–NH2 via an ammonolysis reaction [15, 16]. An incoming amine R3–NH2 results in the formation of an N-substituted amide R1–CO–NH–R3, yielding an enzymatic aminolysis of esters [17, 18]. Peracids of type R1–CO–OOH are formed when hydrogen peroxide is ...
Presentation part1-201210091211
... Under normal physiological conditions, the primary site of carnitine production is in the liver. During lactation, the production of carnitine in the mammary gland increases, apparently at the expense of production in the mother's liver, which is also accompanied by reduced hepatic enzymatic and tra ...
... Under normal physiological conditions, the primary site of carnitine production is in the liver. During lactation, the production of carnitine in the mammary gland increases, apparently at the expense of production in the mother's liver, which is also accompanied by reduced hepatic enzymatic and tra ...
Text S1: General Metabolism
... In summary, both X. nematophila and X. bovienii have metabolic profiles as expected for bacteria capable of being free living, host-associated, and pathogenic by turns. However, there are several unique pathways to each species, including cellobiose transport and presence of a putative virulence-lin ...
... In summary, both X. nematophila and X. bovienii have metabolic profiles as expected for bacteria capable of being free living, host-associated, and pathogenic by turns. However, there are several unique pathways to each species, including cellobiose transport and presence of a putative virulence-lin ...
Nutrition for sport and exercise
... © 2008 Thomson Wadsworth, a part of The Thomson Corporation. Thomson, the Star logo, and Wadsworth are trademarks used herein under license. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. No part of this work covered by the copyright hereon may be reproduced or used in any form or by any means—graphic, electronic, or mechani ...
... © 2008 Thomson Wadsworth, a part of The Thomson Corporation. Thomson, the Star logo, and Wadsworth are trademarks used herein under license. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. No part of this work covered by the copyright hereon may be reproduced or used in any form or by any means—graphic, electronic, or mechani ...
Catabolism and biotechnological applications of cholesterol
... with a great relevance in biology, medicine and chemistry, playing an essential role as a structural component of animal cell membranes. The ubiquity of cholesterol in the environment has made it a reference biomarker for environmental pollution analysis and a common carbon source for different micr ...
... with a great relevance in biology, medicine and chemistry, playing an essential role as a structural component of animal cell membranes. The ubiquity of cholesterol in the environment has made it a reference biomarker for environmental pollution analysis and a common carbon source for different micr ...
rapid acting insulin analogues - The Association of Physicians of India
... minutes before a meal or immediately after a meal, resulting in better postprandial glucose control and less frequent late hypoglycaemia. This is especially important for individuals who have dinner at late hours of the evening or before bedtime, as the prolonged action of regular insulin may influe ...
... minutes before a meal or immediately after a meal, resulting in better postprandial glucose control and less frequent late hypoglycaemia. This is especially important for individuals who have dinner at late hours of the evening or before bedtime, as the prolonged action of regular insulin may influe ...
The metabolic responses of high intensity intermittent exercise in
... Completion of this PhD and thesis would not have been possible if not for the support and guidance of many people. Firstly I would like to acknowledge and thank my supervisors, Associate Professor Alan Hayes and Dr Christos Stathis. To Alan, thank you for taking me on as an honours student and helpi ...
... Completion of this PhD and thesis would not have been possible if not for the support and guidance of many people. Firstly I would like to acknowledge and thank my supervisors, Associate Professor Alan Hayes and Dr Christos Stathis. To Alan, thank you for taking me on as an honours student and helpi ...
Free radical scavenging and antioxidant effects of lactate ion: an in
... at concentrations usually found at rest or during exercise. Lactate concentrations ranged up to 60 mM because such high lactate levels can be found in muscle (22, 29). Different methods were employed to test the lactate effect on free radicals. Two methods were used to determine its scavenging activ ...
... at concentrations usually found at rest or during exercise. Lactate concentrations ranged up to 60 mM because such high lactate levels can be found in muscle (22, 29). Different methods were employed to test the lactate effect on free radicals. Two methods were used to determine its scavenging activ ...
DEVELOPMENT OF LACTIC ACID PRODUCTION
... fermentation of L-(+)-lactic acid (lactate) was carried out using the electrodeionization (EDI) technique. The effect of initial lactate concentrations on microbial growth was initially investigated. A mathematical simulation of the product inhibition was successfully illustrated. It was found that ...
... fermentation of L-(+)-lactic acid (lactate) was carried out using the electrodeionization (EDI) technique. The effect of initial lactate concentrations on microbial growth was initially investigated. A mathematical simulation of the product inhibition was successfully illustrated. It was found that ...
Acid-Base 2013 - UMF IASI 2015
... [HCO3 -] rather than to absolute change in either one •if both PaCO2 and [HCO3 -] change in the same direction, the ratio stays the same and the pH or [H+] remains relatively stable •the alteration in pH occurs when either HCO3 - or PaCO2 changes the other variable in the same direction ...
... [HCO3 -] rather than to absolute change in either one •if both PaCO2 and [HCO3 -] change in the same direction, the ratio stays the same and the pH or [H+] remains relatively stable •the alteration in pH occurs when either HCO3 - or PaCO2 changes the other variable in the same direction ...
Aalborg Universitet metabolic engineering approach
... types of biorefinery systems; the most described type is probably the enzymatic and microbial conversion of lignocellulose to different products, e.g. bioethanol. However, for this type of biorefinery to be economical competitive on the open market, emphasis on high value products like certain chemi ...
... types of biorefinery systems; the most described type is probably the enzymatic and microbial conversion of lignocellulose to different products, e.g. bioethanol. However, for this type of biorefinery to be economical competitive on the open market, emphasis on high value products like certain chemi ...
Metabolic downregulation during diapause in embryos of Artemia
... which they are released into the environment (Clegg and Conte 1980, Qiu and MacRae 2010). These late gastrula embryos are made up of roughly 4000 cells and have a selectively permeable cyst wall which allows only water and gases to diffuse across (Clegg and Conte 1980). When released from the adult ...
... which they are released into the environment (Clegg and Conte 1980, Qiu and MacRae 2010). These late gastrula embryos are made up of roughly 4000 cells and have a selectively permeable cyst wall which allows only water and gases to diffuse across (Clegg and Conte 1980). When released from the adult ...
Osmo- and thermo-adaptation in hyperthermophilic Archaea
... isolated from a variety of hot environments, most species originate from marine geothermal areas, hence they are slightly halophilic. The accumulation of low-molecular mass organic solutes, i. e., compatible solutes, is one of the most common strategies developed by cells to cope with fluctuations o ...
... isolated from a variety of hot environments, most species originate from marine geothermal areas, hence they are slightly halophilic. The accumulation of low-molecular mass organic solutes, i. e., compatible solutes, is one of the most common strategies developed by cells to cope with fluctuations o ...
13C MRS: An outstanding tool for metabolic studies
... C in specific positions have made it possible to follow in vivo and in vitro the activity of a large variety of metabolic pathways in cells, animals, and humans. These include glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis and degradation, gluconeogenesis, the tricarboxylic acid cyc ...
... C in specific positions have made it possible to follow in vivo and in vitro the activity of a large variety of metabolic pathways in cells, animals, and humans. These include glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis and degradation, gluconeogenesis, the tricarboxylic acid cyc ...
Metabolism of heme
... Heme is the prosthetic group of hemoglobin, myoglobin, & cytochromes and so on. - most common porphyrin in humans is heme - one ferrous goup in tetrapyrole ring - heme proteins (hemoproteins) are rapidly synthsized and degraded - 6 to 7 g per day hemoglobin turned over ...
... Heme is the prosthetic group of hemoglobin, myoglobin, & cytochromes and so on. - most common porphyrin in humans is heme - one ferrous goup in tetrapyrole ring - heme proteins (hemoproteins) are rapidly synthsized and degraded - 6 to 7 g per day hemoglobin turned over ...
The Metabolic Functions of Carnitine in Torulopsis
... Pearson & Tubbs (1967) have suggested that carnitine might play a significant role in cellular metabolism by reacting with acetyl-CoA to release CoA and, in this way, buffer the ratio of acetyl-CoA and CoA. In monkey sperm cells Casillas & Erickson (1975) reported a total carnitine concentration 100 ...
... Pearson & Tubbs (1967) have suggested that carnitine might play a significant role in cellular metabolism by reacting with acetyl-CoA to release CoA and, in this way, buffer the ratio of acetyl-CoA and CoA. In monkey sperm cells Casillas & Erickson (1975) reported a total carnitine concentration 100 ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑