* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download pH - Elmwood Park Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
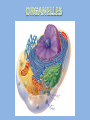
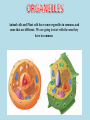
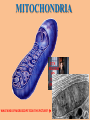
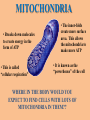
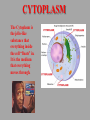
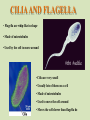
Organelles are a lot like “mini-organs”. They all have jobs, and they all work together to keep the cell alive and functioning properly, just like the organs in your body. Animal cells and Plant cells have some organelles in common, and some that are different. We are going to start with the ones they have in common. THE NUCLEUS • Contains the DNA for the cell • Things move in and out of the nucleus through small holes in the nuclear membrane. • The membrane surrounding the nucleus is called the “nuclear envelope”. • The Nucleolus is in the center of the nucleus, and house the components that make up Ribosomes. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM • The ER are like mini factories inside the cell. •2 types: Smooth and Rough • Smooth ER builds all types of molecules, like lipids and other things the cell needs • Rough ER has Ribosomes on the outside of it, and package the proteins ribosomes make for transport. • ER has many folds that help increase surface area. RIBOSOMES Ribosomes make proteins. They can be found on the outside of the Rough ER, and in the Cytoplasm. GOLGI APPARATUS The Golgi Apparatus takes all the things made by the ER, modifies them, organizes them, and then packages them in vesicles, so they can be shipped off to wherever they are needed in the cell or in the body. MITOCHONDRIA IT’S BIGGER ON THE INSIDE! WHAT KIND OF MICROSCOPE TOOK THIS PICTURE? MITOCHONDRIA • Breaks down molecules to create energy in the form of ATP • This is called “cellular respiration” • The inner-folds create more surface area. This allows the mitochondria to make more ATP • It is known as the “powerhouse” of the cell WHERE IN THE BODY WOULD YOU EXPECT TO FIND CELLS WITH LOTS OF MITOCHONDRIA IN THEM?? CYTOPLASM The Cytoplasm is the jello-like substance that everything inside the cell “floats” in. It is the medium that everything moves through. THE CYTOSKELETON • A support system of proteins that provide structure for the cell, and a way for organelles to move around • Made up of MICROTUBULES and MICROFILAMENTS. THE CYTOSKELETON • MICROTUBULES are hollow, tube-like protein structures that help give the cell shape, and provide a guide for organelles to move along, like railroad tracks. •MICROFILAMENTS are smaller, solid rods that help the cell move. ANIMAL CELL ORGANELLES LYSOSOMES •A membrane filled with digestive enzymes • Responsible for breaking things down CILIA AND FLAGELLA • Flagella are whip-like in shape • Made of microtubules • Used by the cell to move around #tbt #selfie • Cilia are very small • Usually lots of them on a cell • Made of microtubules • Used to move the cell around • Moves the cell slower than flagella do PLANT CELL ORGANELLES VACUOLES • Vacuoles are simple, membranebound sacs • Different vacuoles serve different purposes • Most plant cells have a large central vacuole that stores salts and other chemicals. • Vacuoles store things for the cell, like storage bins, or garbage bags. How can the cell use the central vacuole to regulate cell size?? CHLOROPLASTS Chloroplasts harness the light from the sun to produce sugars for energy via photosynthesis. Organelles work together to accomplish multiple goals, and keep the cell alive. Compare the environment inside the cell to something you are familiar with in real life.











![Student_Work_files/how cells keep us alive[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008096061_1-3bccda7a250f4b6d053f03d6cd844694-150x150.png)


















